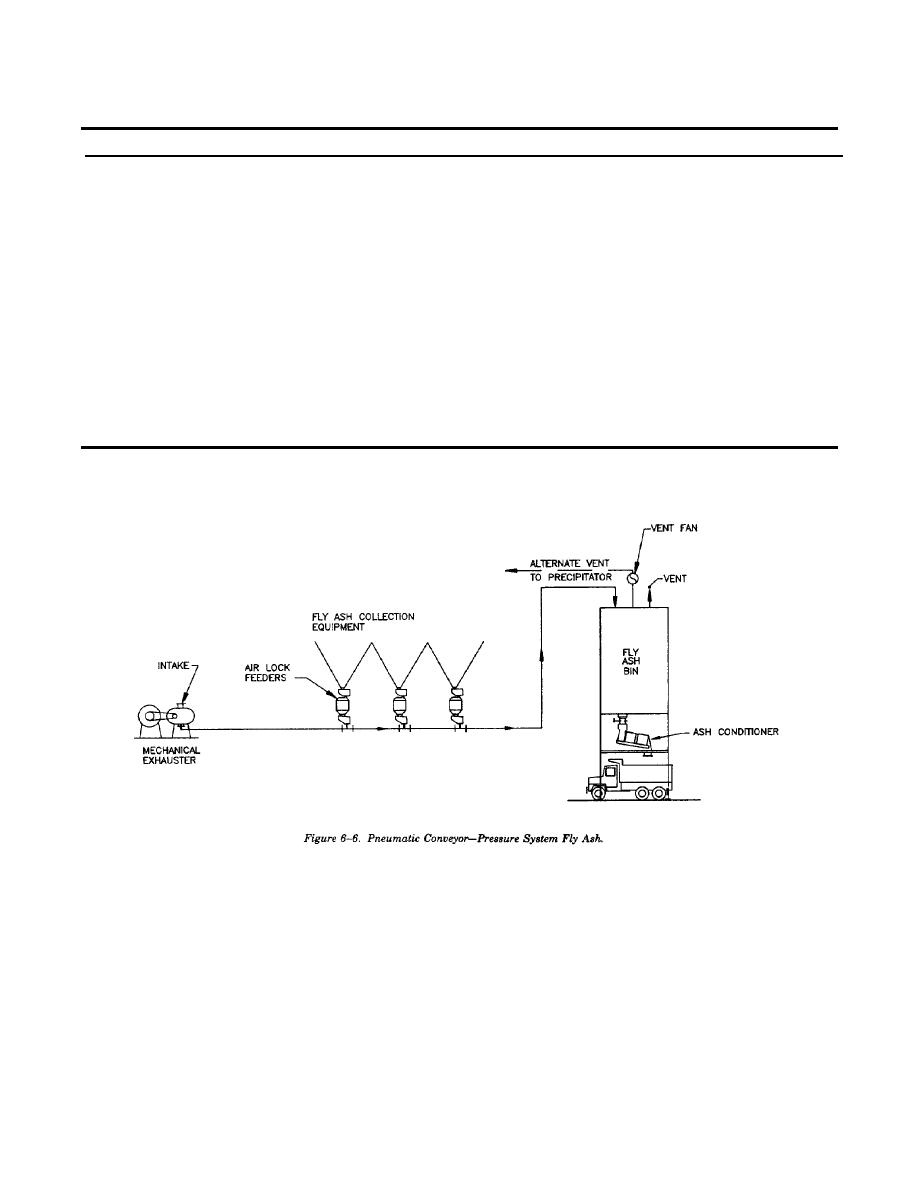
TM 5-810-15
Table 6-1. Comparison of Pneumatic Vacuum Versus Pressure Ash Conveying Systems.
Vacuum Systems
Pressure Systems
When Recommended
Convey systems less than 60 TPH per system.
High system capacity.
Reasonable conveying distance.
Long conveying distances (greater than 1000 to
2000 feet).
Advantages
Less maintenance at hoppers.
Relative unlimited capacity.
System leaks inward for cleaner environment.
Relative unlimited conveying distance.
Multiple collecting points.
No separating equipment.
Simpler control scheme.
Clean air blowers multiple disposal points.
Disadvantages
Requires separating equipment and process bag
Double gates required with air lock.
filter.
Air lock pressurizing and venting requires
Blower life dependent on separating equipment
additional piping and valving.
Ash leaks outward into the plant.
Higher maintenance costs.
most preferable type of control. The PC*s ability to
and timing and gives him the ability to
perform relay logic, timing, counting, and se-
troubleshoot, modify and expand with the system.
quencing functions, provides a way to perform the
(2) Before the advent of the PC, both the
tasks required for ash handling system control. A
bottom ash and fly ash made extensive use of the
number of higher level PC*s also offer more
drum sequencer, electromagnetic timers and
enhanced capabilities such as instruction,
counters, and relay logic. The disadvantage of the
sophisticated report generation and off-line pro-
electromechanical system is the large amount of
gramming. The PC performs all ash handling
relay control required for the drum sequencer; the
controls and allows flexibility in control schemes
periodic maintenance required for the drum se-
giving the user many benefits. The PC has a
quencer, the large amount of panel area required;
memory and is programmable, providing the user
the extensive wiring; and the inflexibility of the
with the ability to change the ash handling sequence
system when changes are required.
6-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
