MIL-HDBK-1025/10
Note
Cover all open pole holes as soon as they are dug, except when the pole
is to be set into the hole immediately after digging.
Setting Poles
7.4.4
CAUTION
Pole setting is a hazardous job even with the best equipment and
experienced personnel. The methods authorized for setting poles are by
piking, using the winch line method, or using a gin pole.
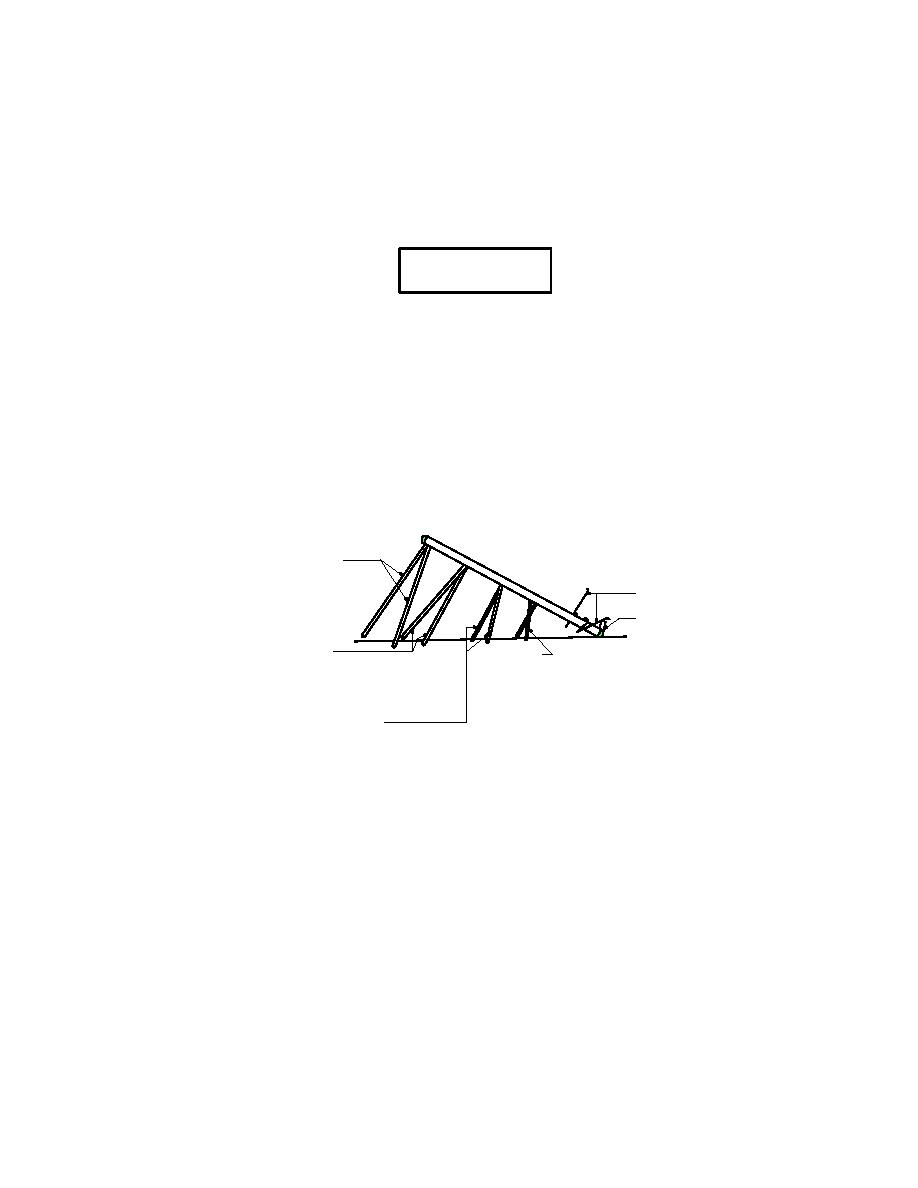
7.4.4.1 Pike Pole Method. Figure 9 illustrates the pike pole method. This is the earliest
method of raising poles and should be employed when a truck cannot be brought in. A jenny
initially supports the pole and a cant hook keeps the pole from rolling. The bumpboard protects
the wall of the hole from being caved in by the pole butt. Pikers, lift the line pole, by punching
into the pole the steel spikes of the pike poles.
HEAVY
PIKERS
4.3 METERS
(16 FEET)
CANT
HOOK
BUMP-
BOARD
5 METERS
(14 FEET)
JENNY
GUIDE PIKERS
3.6 TO 4.3 METERS
(12 TO 14 FEET)
Figure 9
Pike Pole Method
a. Before setting a pole the foreman should ensure a clear working space and verify that
all movable obstacles are removed from the area. Personnel should not wear safety harnesses and
climbers when setting poles. Tools or other items may not be substituted for bumpboards.
Always use a jenny to support the pole until it is high enough to use pikes. Only experienced
workers should use the jenny. The angle of contact between the pole and jenny should be
maintained as close to 90 degrees as possible.
b. At least three experienced pikers should be used in addition to the supervisor. The
number of pikers required increases with the pole length as shown on Table 38. One person
should handle the butt of the pole and a minimum of two side pikers are needed. Inexperienced
workers used in this work should be thoroughly instructed on the hazards involved. A two-
76



 Previous Page
Previous Page
