UFC 4-021-02NF
27 September 2006
change 1, 23 October 2006
5-6.2
For the purpose of demonstrating the application of different approaches, two
alternatives for meeting the project requirement are presented. While an individual
component probability of detection may not meet a more demanding specification,
layering or combining components can result in a higher overall system probability of
detection as illustrated below:
5-6.2.1 Option A: Use a microwave perimeter system with a Pd of 99%. The
equipment and system meets the project objectives and no other IDS methods are
technically required to meet the specified intrusion detection range.
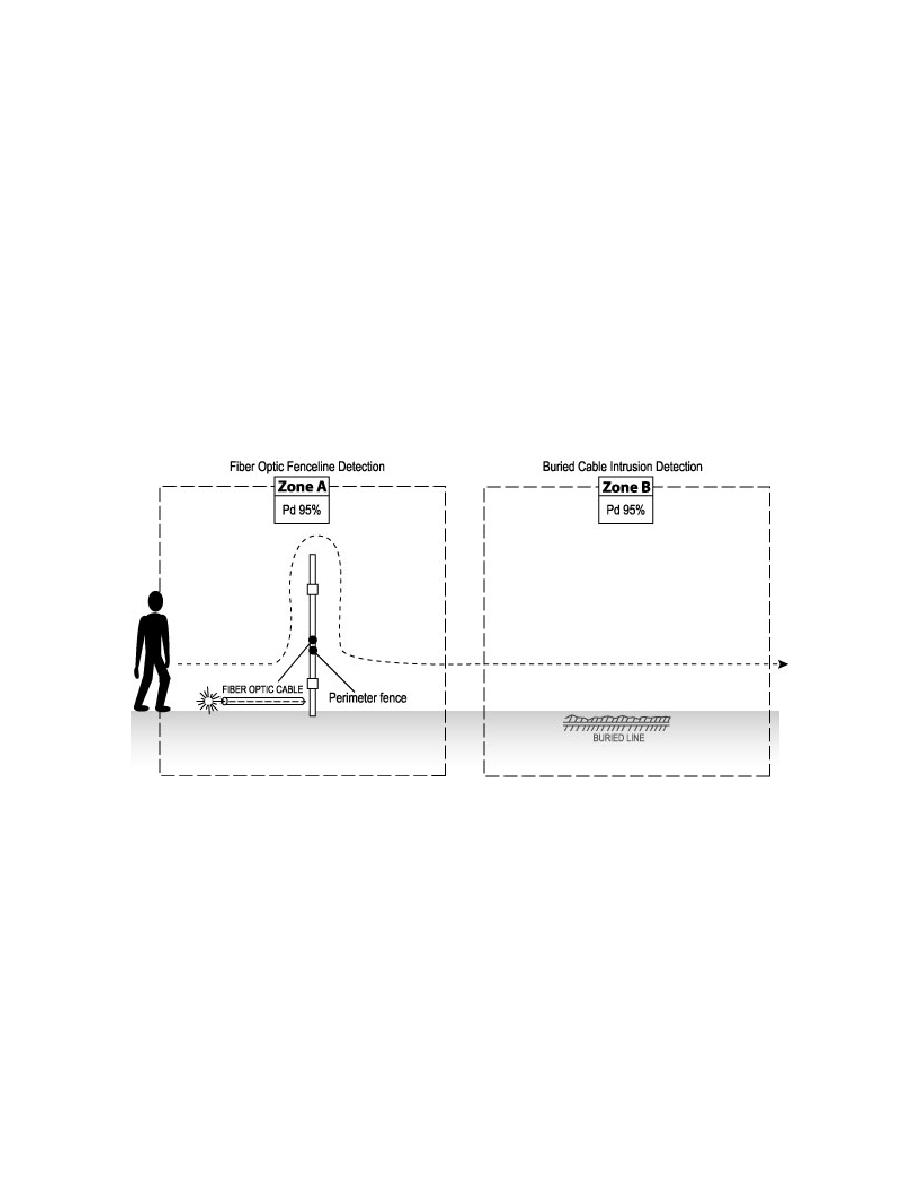
5-6.2.2 Option B: If the scenario is such that terrain contour makes microwave
technology unfeasible, the IDS designer could consider a zoned approach of combining
a fence mounted fiber-optic detection system with a buried cable detection system as
shown in Figure 5-13.
Figure 5-13. Zoned Detection System
5-6.3
If the two detection systems shown in Figure 5-13 are integrated in an
electrical "OR" logic, an alarm from either system results in an IDS alarm. The resultant
net Pd can be calculated as follows:
(Pd)A = 95%; therefore the probability of not being detected is (1-Pd)= 1-0.95= 5%
The probability of not being detected in Zone B is similarly calculated as 5% as well.
94



 Previous Page
Previous Page
