UFC 4-023-03
25 January 2005
The building incorporates a normal weight brick veneer. Based on the self
weight of the described members and specified (averaged) live loads for the design (live
loads are not reduced for tie forces), the following loads (unfactored) were defined for
tie force development:
D = 23 psf;
L = 55 psf
F-2.2
Required Tie Forces.
For the purposes of illustration, these "averaged" loads were used to calculate
tie forces, to develop tie schemes, and to generate ties and connections. From Section
7-2, internal horizontal, external wall horizontal, peripheral and vertical tie force
capacities were calculated and are presented in Table F-1:
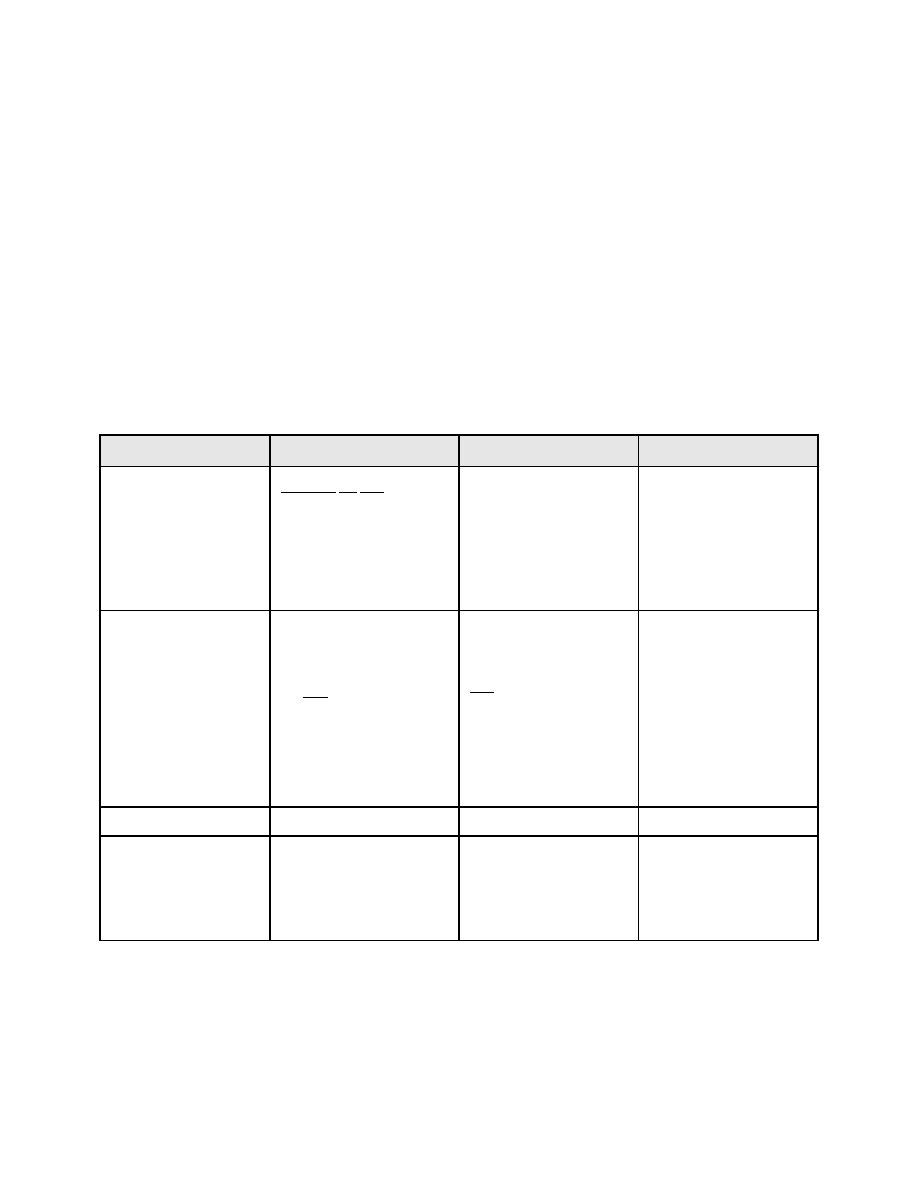
Table F-1 Required Tie Forces for Barracks Building
Tie Force
Equation
Parameters
Required Tie Force
(D + L) lr
D = 23 psf
TFint n-s = 0.89kips / ft
Internal horizontal,
1.0
Ft
TFi
L = 55 psf
TFint e-w = 0.80kips / ft
65 15 3.3
lr = 14 ft
Ft = lesser of:
1.63 + 0.33no or
n0 = 3
4.92
Ft = 2.63
2Ft = 5.26kips
TFew = 1.17kips / ft
Greater of:
Horizontal to
The lesser of:
external walls,
= 12
l
ft
2.0Ft or
s
TFew
(note: internal ties
ls
assumed to function as
ls
Ft = 3.85kips
Ft
external wall ties if tied
8.2
8.2
to peripheral tie)
3% of factored vertical
and
load =
3% of max factored
2.5 kips at columns
vertical load carried by
the wall at the floor level:
TFp = 2.63kips
Peripheral, TFp
Ft
TFv = 1.5kips / ft
capacity equal to the
(based on max load
Vertical, TFv
maximum design ultimate
combination of
dead and live load
1.2D+1.6L)
received by the wall or
column from any one
story
F-2.3
Tie Force Connections.
Tie force "schemes" for each of the required force systems can be postulated
and designed or checked as follows:
F-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
