TM 5-840-2
CHAPTER 2
WAREHOUSES
2-1. General.
point load such as wheel loads from forklift trucks,
wheel loads from trailers backed into the building,
Warehouse design discussed in this manual is
or any type of movable storage bin on legs. Truck
intended to provide a dry environment for the
loads within warehouses shall be taken as HS 20-44
purpose of storing goods and material that require
loadings of the HB-13, Highway Bridges, published
protection from the elements. Warehouses must be
by the American Association of State Highway and
designed to accommodate the loads of the material
Transportation Officials (AASHTO). Loads on
to be stored, the associated handling equipment,
railroad tracks within warehouses shall conform to
and the needs of the operating personnel. The
American Railway Engineering Association
design of the warehouse space should be planned to
(AREA) E-80 loading. Concentrated live loads due
best accommodate the physical dimensions of the
to forklift wheels can be calculated from mass
material to be stored. The different types of
(weight) data obtained from the forklift
warehouses generally associated with storage de-
manufacturer plus an account of the loads this
pots include heated and unheated warehouses,
vehicle is expected to carry.
refrigerated warehouses, and controlled humidity
(2) Uniformly distributed live loads are deter-
(CH) warehouses.
mined from the type of occupancy expected for the
2-2. Structural requirements.
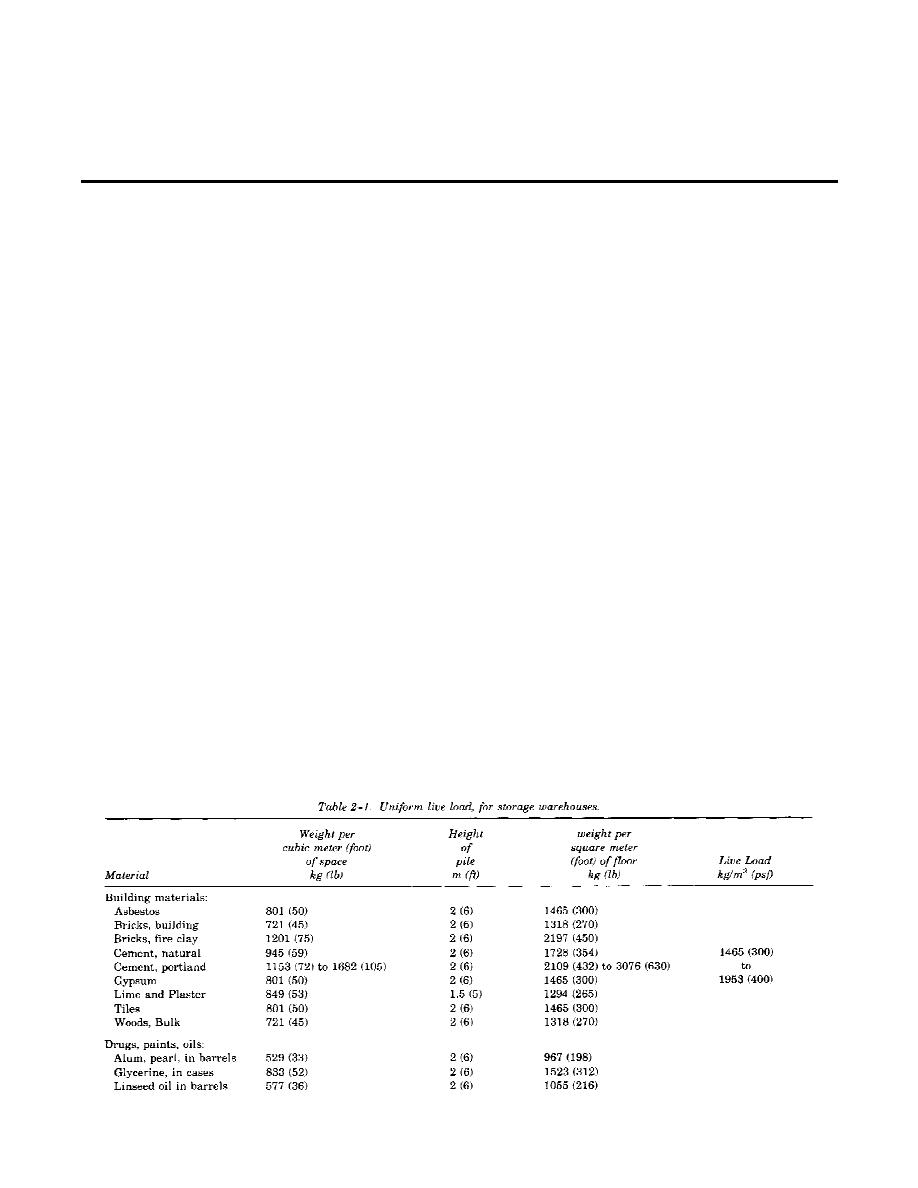
floor. Masses (weights) of materials typically stored
in warehouses are given in table 2-1. Live load
Design of warehouse structures is to be based on
pressures should be calculated for the maximum
the dead and live load requirements of the structure
loading condition that the warehouse is expected to
as it will be built. Snow, wind, and seismic loads
experience in its lifetime. Quite frequently the type
shall be considered where they are applicable.
of material stored in a warehouse will be different
a. Dead load requirements. In general, the dead
from that for which it was originally designed. If
loads shall be calculated from the weights of all
the material stored is beyond design loads, cracking
fixed components of the structure including fixed
and settlements can occur in the slab and
pieces of equipment. Refer to the values given in
foundation. As a precautionary measure, the
TM 5-809-1/AFM 88-3 Chap. 1, chapter 3, section
maximum live load pressure for each building area
3 for weights of building materials.
in kilograms per square meter (pounds per square
b. Floor live load requirements. Live loads to
foot) should be displayed on plaques or walls. For
be considered are concentrated wheel loads and
design of floors due to heavy loads refer to TM 5-
uniformly distributed loads, as applicable.
809-12/AFM 88-3, Chap. 15.
(1) Concentrated loads pertain to any movable
2-1



 Previous Page
Previous Page
