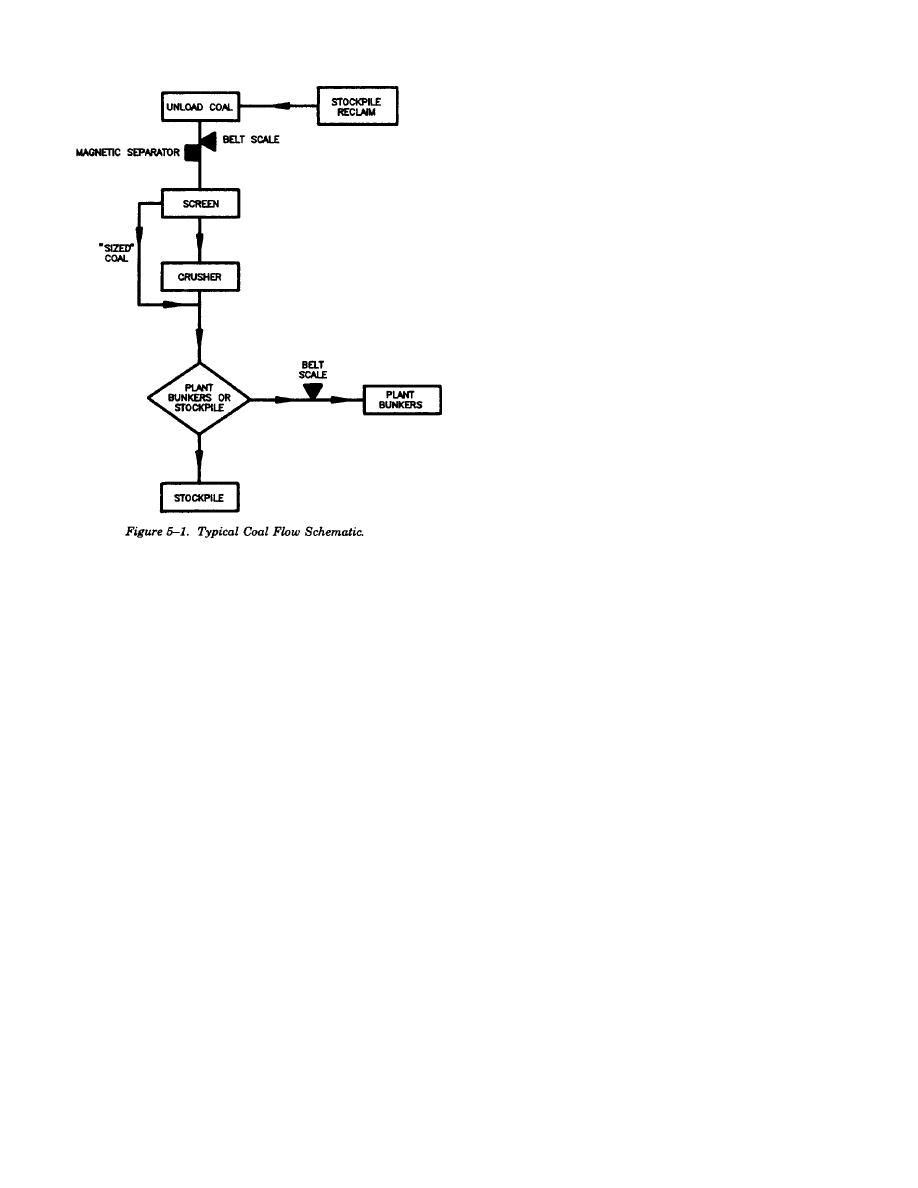
TM 5-810-15
over the life of the plant. One and one-half shifts
per day of running time for a coal handling system
at full mobilization would be a reasonable criteria
to use.
(1) The conveyor should be operating with
the belt fully loaded and at minimum speed for the
required amount of material to be handled per hour.
There is no advantage to be gained by running
conveyors at high speed while only partly loaded.
(2) The full load on the belt will be
considered as approximately 80 percent of the
cross sectional load area of the conveyor belt which
must take into account that load carrying width is
several inches narrower than the actual belt width.
(3) Maximum belt speed for 24, 30 and 36
inch wide conveyors will not exceed 600 fpm and
maximum 800 fpm for 42, 48, 54 and 60 inch wide
belts and maximum 1,100 fpm for 72-inch wide
belts that carry coal. Wider belts should be limited
to 600 fpm if possible. Conveyor belts smaller than
24 inches wide will not be used.
d. Coal characteristics and constituents. Design-
ing for a single homogeneous coal type is generally
no longer feasible. Where multiple coals will be
burned, the conveyer designer must consider the
worst case for his or her design based on coal
b. Climatic conditions. Annual temperature ex-
ranking (according to ASTM standards), particle
tremes, rainfall, seismic zone and wind conditions
size and shape (sieve analysis), coal density, mois-
will all affect coal handling equipment selection.
ture content, corrosiveness and abrasiveness, sul-
Hostile equipment environments can dictate what
phur content, angles of repose and surcharge, safe
type of conveying system is to be selected.
angle of incline, and coal grindability index. Each
c. Coal conveying rate. The design conveying
factor or combination of factors can dictate the
rate of the coal handling system depends on the
type or size of crusher, transfer chute or conveyor
maximum daily coal burn rate of the steam plant,
that can safely be used to handle the material. The
including future increases in coal requirements due
physical and chemical characteristics of coal make
to plant expansion. Maximum daily coal re-
it one of the more difficult bulk solids to handle.
quirement is computed by using the maximum
Care must be taken by the designer to make sure
continuous ratings of all the boilers and conserva-
that he is fully aware of the properties of the coal
tive values for boiler efficiency and coal heating
that is to be handled. A system designed for a
values. Once the maximum daily coal burn rate is
western subbituminous coal will not be suitable for
established, the maximum allowable operating time
an eastern coal, and due to the variable
per day must be defined to arrive at the design
constituents, each different type of coal will have a
conveying rate. It is general industry practice to
direct influence on air pollution devices, boiler and
select the design conveying rate of the coal
equipment design and material handling equipment
handling system so it can transport the maximum
design.
e. Conveying western coal.. Because of the in-
daily coal requirements to the steam plant in a
single eight hour shift allowing seven hours of
creasing use of western, low-sulfur coal in recent
actual operation time. This criteria allows coal to
years, the designer must take into account that
be handled during the daylight hours and provides
equipment sized to handle a given quantity of
adequate time for maintaining the equipment in
eastern coal cannot usually handle the same quan-
good operating condition. The amount of running
tity of western coal, even though the conveyor has
time for an Army Ammunition Plant (AAP) should
been sized to handle the lower density and sur-
not be confined to the eight-hour per day limitation.
charge angles of western coals. This is partly due to
The amount of time that the AAP would be
the vastly different range of flow characteristics
operating at the full mobilization condition has
that are inherent in western coal. A rule of thumb
historically been for relatively short periods of time
for sizing conveyors for western coal is to go one
5-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
