TM 5-810-15
of condensate available as feedwater is to be
water where they regulate the undesirable effects of
established. From this information the actual
water impurities. Blowdown is used in the
feedwater constituents to be treated can be deter-
evaporative process to control the concentration of
mined. The water treatment requirements for the
dissolved and suspended solids. Methods of water
plant can then be identified based on the allowable
treatment include filtration (reverse osmosis),
boiler water limits and the desired amount of
deaeration (para 7-3 above) and degasification,
continuous boiler blowdown (use 1 percent of
cold or hot lime softening, sodium zeolite ion
boiler maximum continuous rating as a starting
exchange, chloride cycle dealkalization, deminera-
blow-down value).
lization, internal chemical treatment, and blow-
down. Several internal treatment methods com-
monly used to treat boiler water include phosphate
Table 7-6. General Raw Water Analysis.
hydroxide or conventional treatment method, che-
lent method, polymer method (feedwater < 1.0
Milligrams/Liter
ppm Ca as Ca CO3), and coordinated phosphate/pH
As the ion or as
(high purity # 15 mirohms conductivity). These
Water properties
Shown
chemical internal treatment methods can be used in
conjunction with external treatment methods. After
Calcium
64.5
a raw water analysis has been made, a water
Silica
9.1
treatment specialist should be consulted and an
Magnesium
20.7
evaluation should be made on the practicability of
Sodium
70.0
a combination of internal and external treatment
Sulfate
182.0
methods. It is usually more cost effective to
Chloride
23.3
externally pretreat the feedwater as much as
Bicarbonate
211.0
practical. This discussion concerns boiler feedwater
Nitrate
4.0
treatment equipment. It is assumed that water
Total hardness
248.0
delivered to the feedwater equipment is of a
Carbonate hardness
173.0
pretreated, clear, potable quality free of organic
Noncarbonate hardness
73.0
materials.
Total alkalinity
166
d. Boiler feedwater treatment equipment. The
Conductivity - microseim per
731
industry standards for reducing water constituents
per centimeter
in boilers with an operating pressure of 400 psig
pH
8.2
are reverse osmosis, ion exchangers, or combina-
tions of the two.
Note: Water characteristics will vary by location.
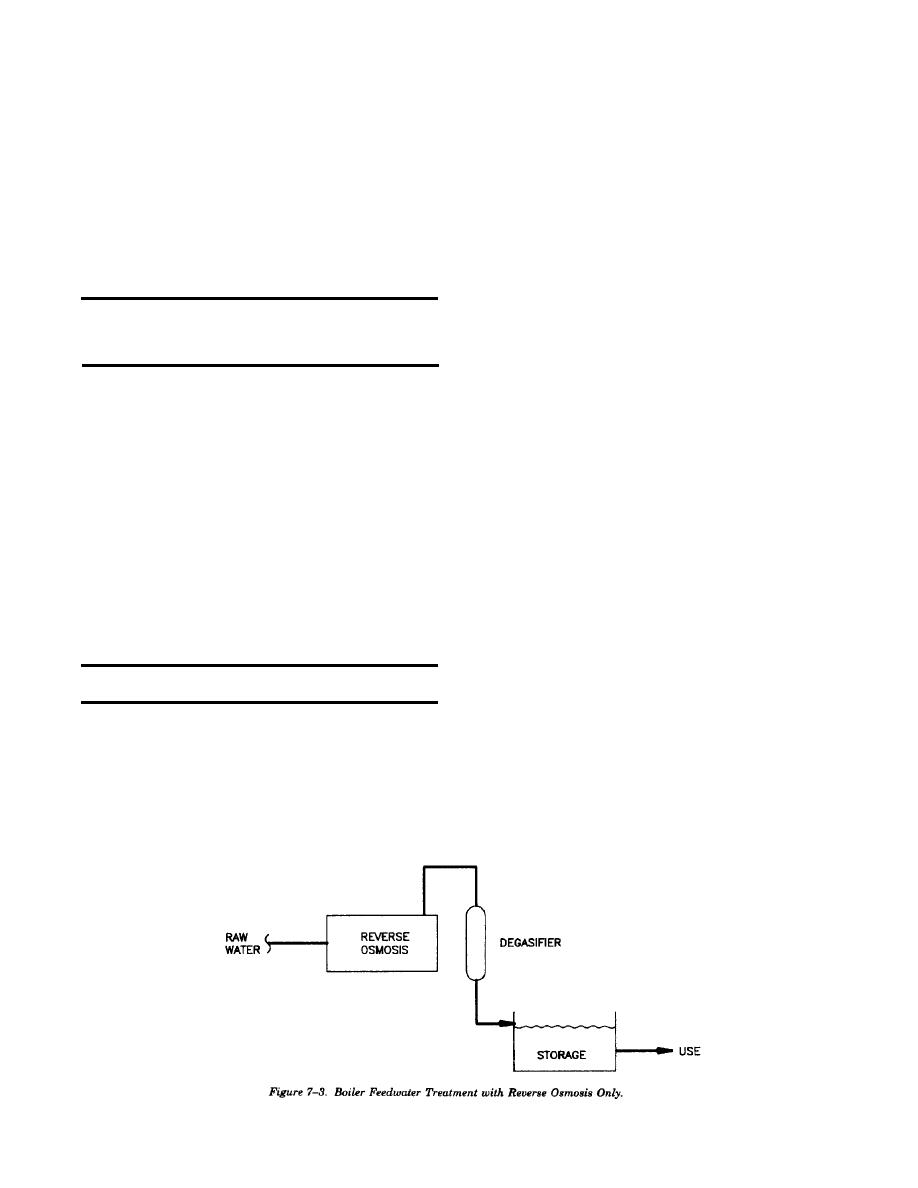
(1) Reverse osmosis (RO) is a filtration
method which removes approximately 90 percent
c. Treatment. Water treatment is generally cate-
of all inorganic dissolved solids from the feedwater.
gorized by external treatment or internal treatment.
Reverse osmosis can be used alone, as shown in
External treatment dampens, softens, or purifies
figure 7-3, but is more generally used with regen-
raw water prior to introducing the water into the
erative ion exchange equipment (demineralizer) as
feedwater system. Internal methods introduce
shown in figure 7-4. The viability of using reverse
chemicals directly into the feedwater or boiler
osmosis will be determined by a LCCA.
7-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
