TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
particles, they are usually designed for low inlet
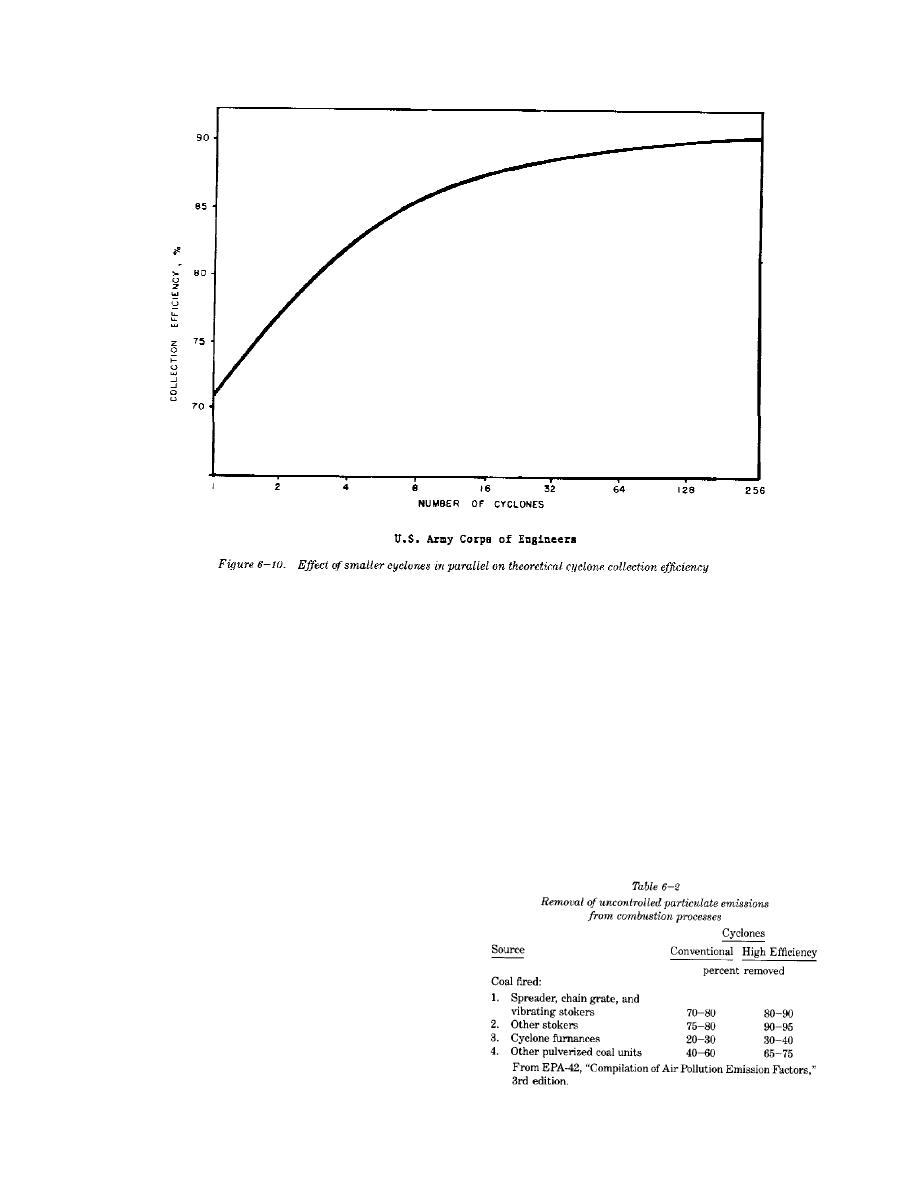
of changing the dimensions of an 8 inch diameter
velocities 5-10 feet per second (ft/sec). This is done to
cyclones is shown in figure 6-11. The effects of
minimize erosion on the cyclone walls and to minimize
changing gas inlet velocity, grain loading, particle
breakdown of coarser particles that would normally be
specific gravity, gas viscosity, and particle size
separated, into particles too fine for collection.
distribution on a 50 inch diameter cyclone are shown
e. Limited space. In cases where cyclones must be
in figures 6-12 and 6-13. These figures illustrate the
erected in limited space, smaller diameter multi-
dependence of cyclone collection efficiency on those
cyclones have an obvious space advantage over larger
variables and the importance of maintaining proper gas
diameter units. Small cyclones also have the advantage
inlet conditions.
b. Field performance. The actual in-field perfor-
of increased efficiency over a single unit handling the
same gas capacity, although this advantage is some-
mance of cyclone units will vary because of changes in
times lost by uneven gas distribution to each unit with
operating conditions such as dust load and gas flow.
resultant fouling of some elements.
Table 6-2 illustrates the optimum expected perform-
ance of cyclone units for particulate removal
6-6.
Cyclone performance
application in combustion processes.
a. Collection efficiency and pressure drop. For any
given cyclone it is desirable to have as high a collection
efficiency and as low a pressure drop as possible.
Unfortunately, changes in design or operating variables
which tend to increase collection efficiency also tend to
increase pressure drop at a greater rate than the collec-
tion efficiency. Efficiency will increase with an increase
in particle size, particle density, gas inlet velocity,
cyclone body or cone length, and the ratio of body
diameter to gas outlet diameter. Decreased efficiency
is caused by an increase in gas viscosity, gas density,
cyclone diameter; gas outlet diameter; and inlet widths
or area. The effect on theoretical collection efficiency
6-12



 Previous Page
Previous Page
