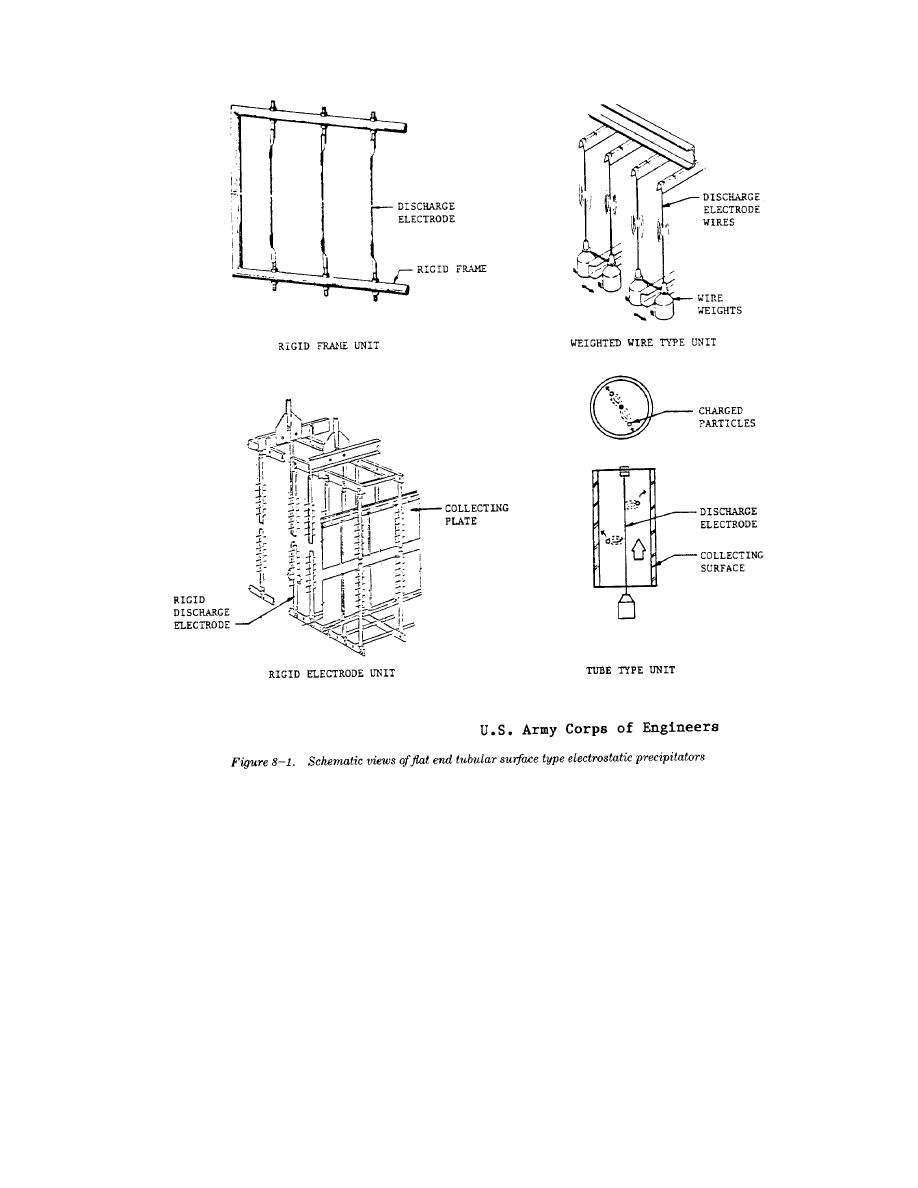
TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
c. Incinerator application. Until relatively recently,
they are most easily retrofitted. In the design of new
installations, the use of hot precipitators has become
ESPs were used for pollution control on incineration
more common, because of the greater use of lower
units only in Europe. In the United States, however, the
sulfur fuels. Low sulfur fuels have higher particle
ESP is now being viewed as one of the more effective
resistivity and therefore particulate emissions are more
methods for the control of emissions from incinerators.
difficult to control with cold precipitation. Figure 8-2
The major problem associated with the use of
may be used for estimating whether hot precipitators or
precipitators on incinerators is high gas temperatures.
cold precipitators should be selected for a particular
Temperatures up to 1800 degrees Fahrenheit can be
sulfur content of coal.
encountered at the incinerator outlet. These tem-
b. Wood refuse boiler applications. An ESP can be
peratures must be reduced before entering a pre-
used for particulate collection on a wood fired boiler
cipitator. Several methods can be used to accomplish
installation if precautions are taken for fire prevention.
this temperature reduction:
The ESP should be preceded by some type of
-- mixing of the gas with cooler air;
mechanical collection device to prevent hot glowing
-- indirect cooling such as waste heat boilers,
char from entering the precipitator and possibly starting
-- evaporative cooling in which droplets of
a fire.
water are sprayed into the gas.
8-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
