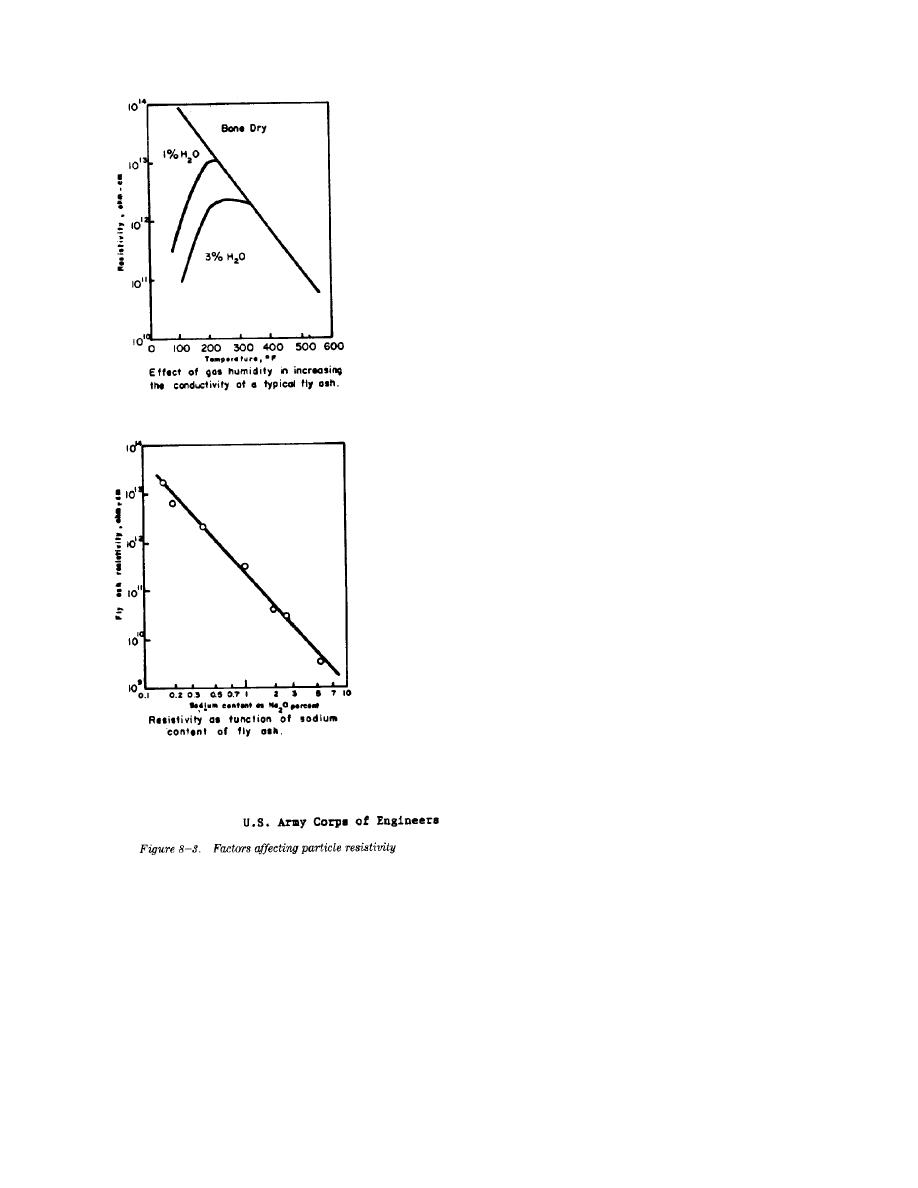
TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
safe rodding out the hoppers should they become
plugged.
e. Rappers. Rappers are used to remove dust from
the discharge and collection electrodes. Rappers are
usually one of two types, impulse or vibrator. The
vibrator type removes dust from the discharge elec-
trode by imparting to it a continuous vibration energy.
They are used to remove dust from the collection elec-
trodes. Impulse rappers consist of electromagnetic
solenoids, motor driven cams, and motor driven ham-
mers. Important features to note in choosing rappers
are long service life without excessive wear and
flexible enough operation to allow for changing
precipitator operating conditions. Low intensity
rapping of plates (on the order of one impact per
minute) should be used whenever possible to avoid
damage to the plates. visual inspection of the effect of
rapping on reentrainment is usually sufficient to
determine a good rapping cycle.
serve both to support the discharge electrode frame
and also to provide high voltage insulation. The mate-
rials used are ceramic, porcelain, fused silica and
alumina. Alumina is the most common. The insulators
must be kept clean to prevent high voltage shorting and
resultant equipment damage. Compressed air or steam
can be used for this purpose.
g. Four point suspension. Rigid electrode and rigid
frame units may utilize a four point suspension system
to support the discharge electrode framework in each
chamber. This type of suspension system assures a
better alignment of the discharge and collection elec-
trodes. This in turn provides a more consistent opera-
tion.
h. Distribution devices. Perforated plates, baffles or
turning vanes are usually employed on the inlet and
outlet of an ESP to improve gas distribution. Improper
distribution can cause both performance and corrosion
problems. These distribution devices may require rap-
pers for cleaning.
i. Model testing. Gas flow models are used to deter-
mine the location and type of distribution devices. The
models may include both the inlet and outlet ductwork
in order to correctly model the gas flow characteristics.
Gas flow studies may not be required if a proven pre-
Hoppers must be sized so that the amount of dust
cipitator design is installed with a proven ductwork
collected over a period of time is not great enough to
arrangement.
overflow and be reentrained. Seals also must be pro-
8-7 Control systems
vided around the outlet to prevent any air leakage. If
The electric power control system is the most impor-
the precipitator is wet, the hopper should allow
tant component system of any E SP. The basic compo-
removal of sludge in a manner compatible with the
nents of this system are: step-up transformer; high
overall removal system. In general the collected dust in
voltage rectifier; voltage and amperage controls; and
the hoppers is more free flowing when kept hot. The
sensors.
hop-pers should be insulated and should have heaters
a. Automatic power control. By utilizing a signal
to maintain the desired temperatures. Hoppers heaters
from a stack transmissionmeter the power level in the
will also prevent the formation of acids that may occur
precipitator can be varied to obtain the desired perfor-
at low temperatures. Provisions should be made for
mance over a wide range of operating conditions.
8-5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
