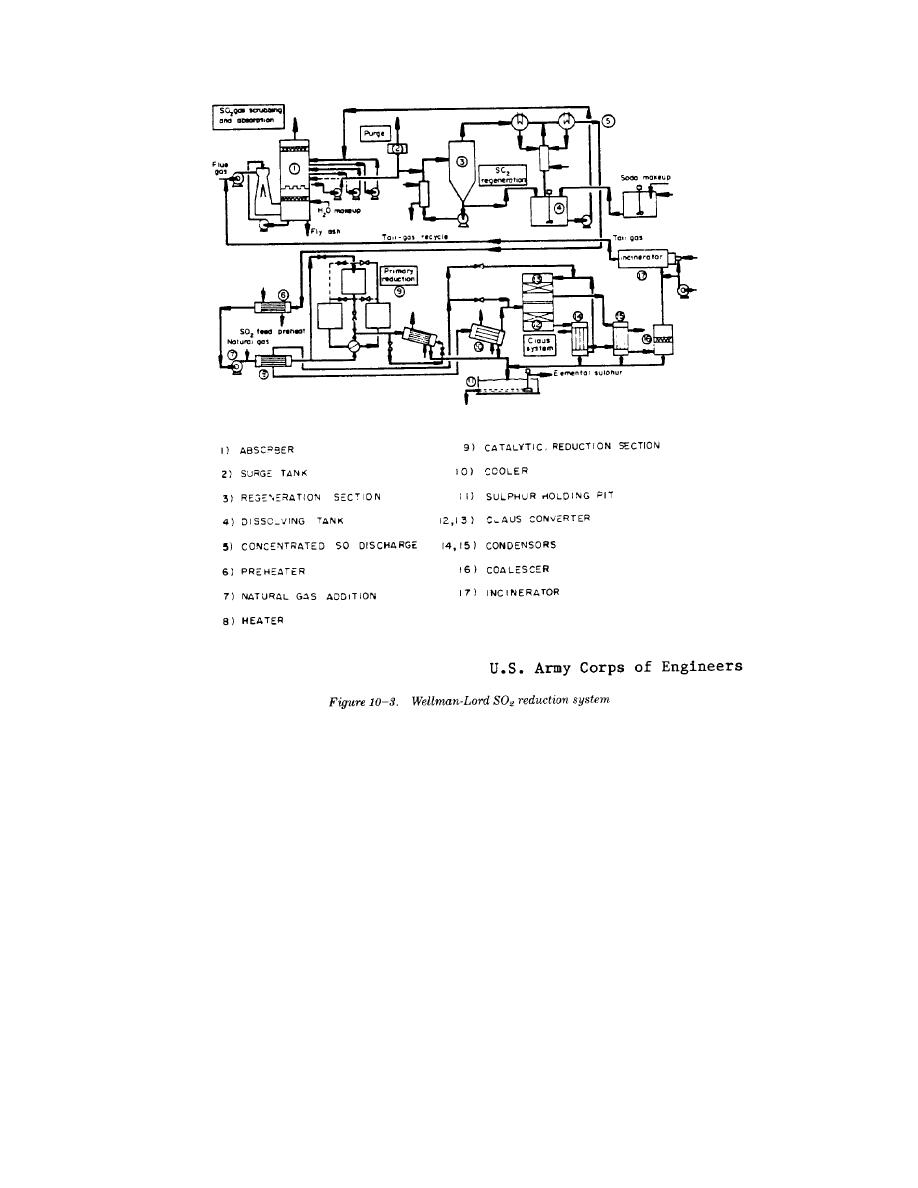
TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
to attrition, chemical decomposition, serious
subsequently store it as a sulphate in the pores
corrosion problems, and danger of
of the zeolite.
v. Cost of flue-gas desulfurization. The actual
combustion of the reactivated carbon.
(2) Zeolites are a class of highly structured alumi-
capital and operating costs for any specific installation
num silicate compounds. Because of the reg-
are a function of a number of factors quite specific to
ular pore size of zeolites, molecules of less
the plant and include:
than a certain critical size may be
-- Plant size, age, configuration, and locations,
incorporated into the structure, while those
-- Sulfur content of the fuel and emission
greater are excluded. It is often possible to
control requirements,
specify a certain zeolite for the separation of
-- Local construction costs, plant labor costs,
a particular material. Zeolites possesses
and cost for chemicals, water, waste disposal,
properties of attrition resistance, temperature
etc.,
stability, inertness to regeneration techniques,
-- Type of FGD system and required equipment,
and uniform pore size which make them ideal
-- Whether simultaneous particulate emission
absorbents. However, they lack the ability to
reduction is required.
catalyze the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 and thus
10-3.
Procedure to minimize SOX emission
cannot desulfurize flue-gases at normal
a. Efficiency requirement. The SOx removal effi-
operating temperatures. Promising research is
under way on the development of a zeolite
ciency necessary for any given installation is dependent
material that will absorb SO2 at flue-gas
upon the strictest regulation governing that installation.
temperatures by oxidation of SO3 and
Given a certain required efficiency, a choice can be
10-7



 Previous Page
Previous Page
