UFC 3 -520-01
June 10, 2002
12-2.4
A more commonly used method of evaluating voltage unbalance that does
not require knowledge of symmetrical components is as follows:
Maximum Phase Deviation from Average Voltage
Percent Unbalance =
100%
Average Voltage
EXAMPLE: Assume that phase voltages are 460, 464, and 450. The average
phase voltage is 458. The maximum deviation from the average voltage is 8
volts and the percent unbalance is given by:
8
Percent Unbalance =
100% = 1.75%
458
12-2.5
Either of the above methods are acceptable for evaluating voltage unbalance.
If the percent unbalance exceeds 3 percent, evaluate the electrical system in more
detail to determine if corrective action is necessary.
12-2.6
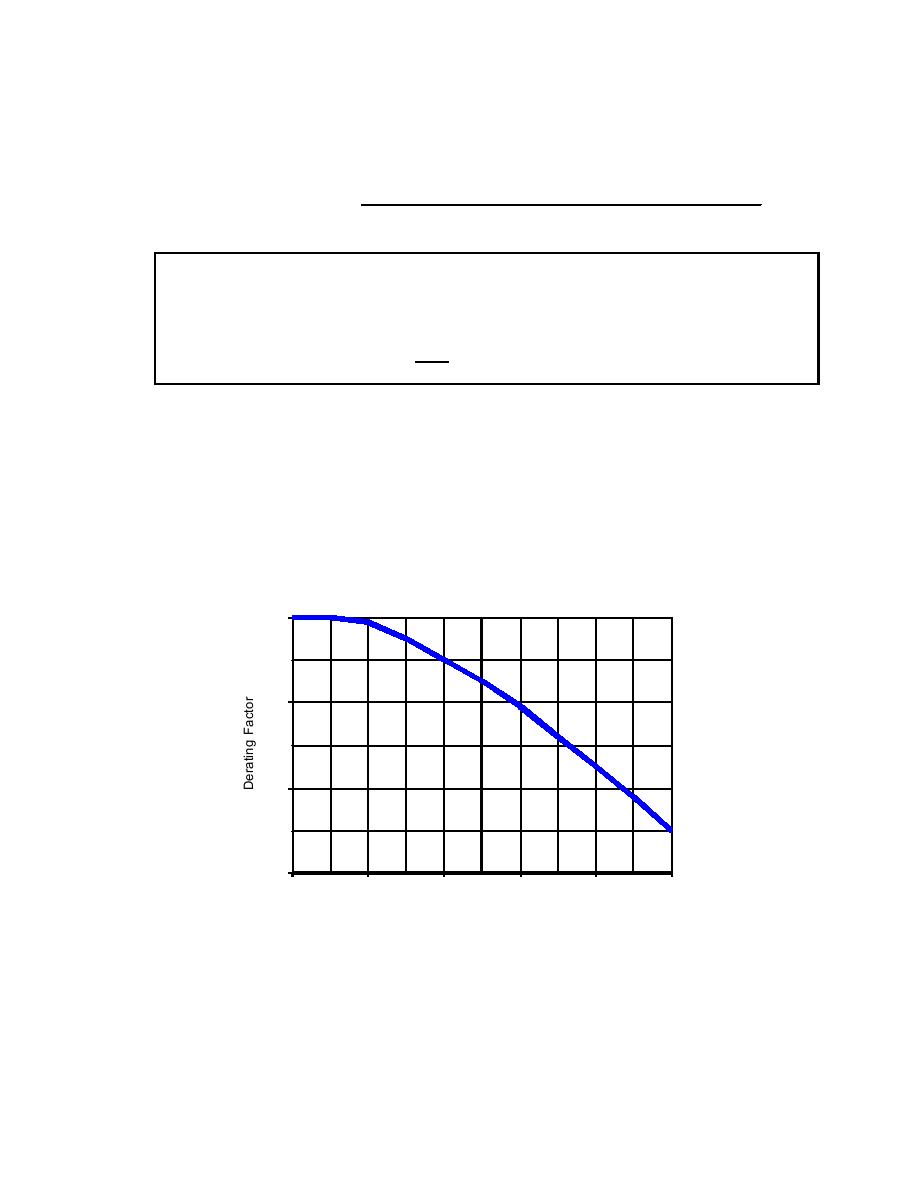
The rated load capability of three-phase equipment is normally reduced by
voltage unbalance. For example, Figure 12-1 shows a typical derating factor for three-
phase induction motors as a function of voltage unbalance.
Figure 12-1. Typical Derating Factor for Three-Phase Induction Motors
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0
1
2
3
4
5
Percent Voltage Unbalance
12-3
HARMONIC DISTORTION EVALUATION .
12-3.1
If a significant number of nonlinear loads are installed in the facility, perform a
harmonic distortion evaluation during the facility design phase. If the effect of nonlinear
loads is expected to be minor, a detailed harmonic distor tion evaluation is not required.
Monitoring of the electrical system power quality is recomme nded to ensure that
harmonic distortion limits are not exceeded.
12-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
