UFC 3 -520-01
June 10, 2002
Notice that the 2 percent impedance transformer has 5 times the short circuit
current of the 10 percent impedance transformer. The 2 percent impedance
transformer might require a complete redesign of downstream electrical
equipment to withstand the higher short circuit cur rents.
B-4.2
Impedance affects transformer regulation. As the impedance increases, the
voltage regulation tends to increase. Voltage regulation is defined as the voltage
change from no load to full load conditions:
Vno - load - Vfull - load
Regulation (percent) =
100%
Vfull -load
B-5
TRANSFORMER SIZING. The following example illustrates the sizing
process for a simple transformer installation. Primary and secondary conductor sizes
are also determined.
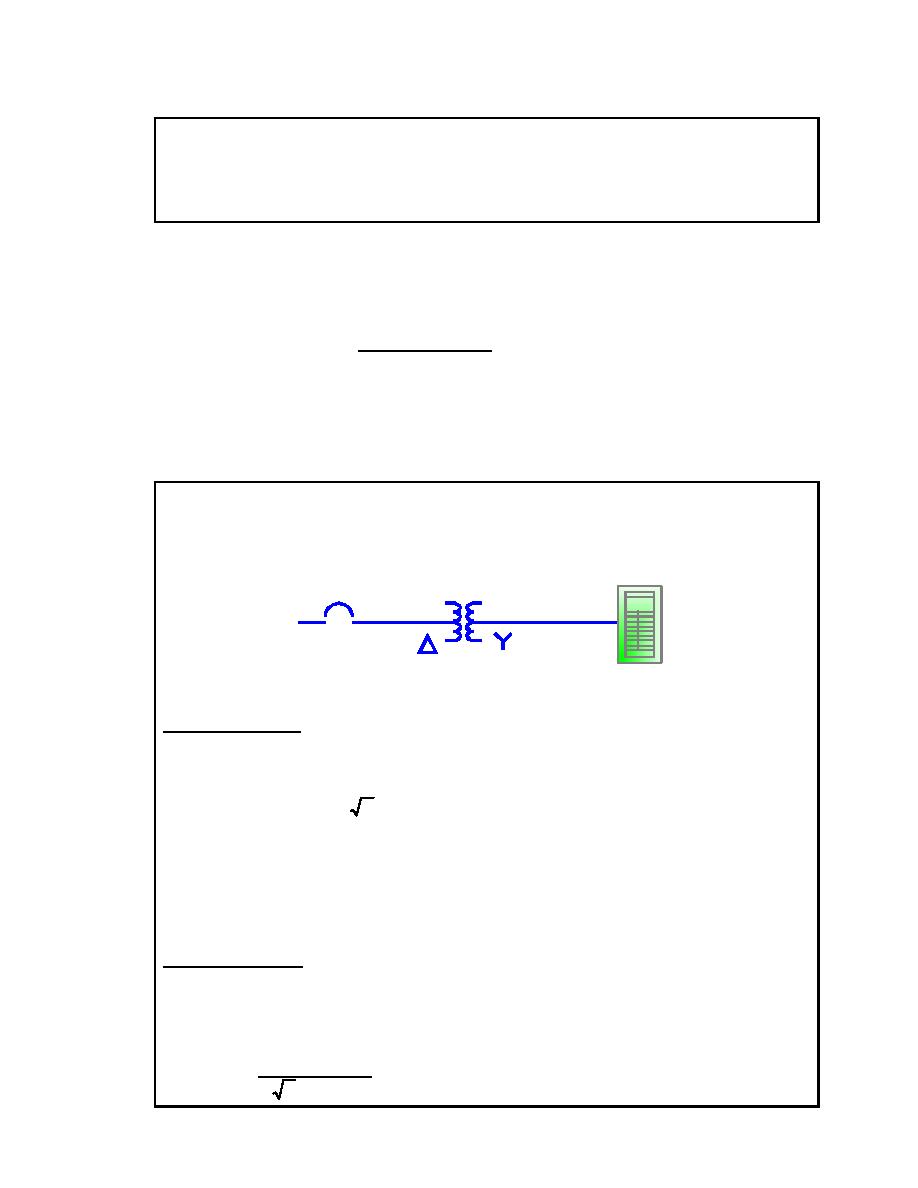
EXAMPLE: A feeder supplies three-phase power to a 480 volt transformer. The
transformer steps down to 208Y/120 volts to a lighting panel with a continuous
load of 30 amperes on each phase. What is the required transformer kVA
capacity, and required amperage on the primary and secondary?
480 V
208Y/120 V
3-Phase
Transformer
Transformer Size
The transformer required kVA capacity is given by:
Required kVA = 3 208 30 = 10.8 kVA
Transformers are provided in standard sizes. The next larger standard size
above 10.8 kVA is 15 kVA. So, choose a 15 kVA transformer for this load. If
additional load growth is anticipated, a larger transformer might have been
selected instead.
Primary Ampacity
Assume that the transformer will eventually be fully loaded. The required primary
amperage is:
15 kVA 1000
Ip =
= 18 amperes
3 480 V
B-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
