MIL-HDBK-1025/10
combustion engine exhausts. Hydrogen chloride can result from faults or fires involving polyvinyl
chloride (PVC) conduits or PCB oils. Adequate oxygen may be unavailable when the atmosphere
is displaced by heavier-than-air gases.
Reminder of Electrical Hazards in the Field. Always identify the electrical
4.3
hazards applying to the work being done. Rules, apparel, tools, and tests, if correctly used, will
protect you from the destructive effects of electric shocks, arcs, and blasts and the hazards of
elevated and confined workplaces.
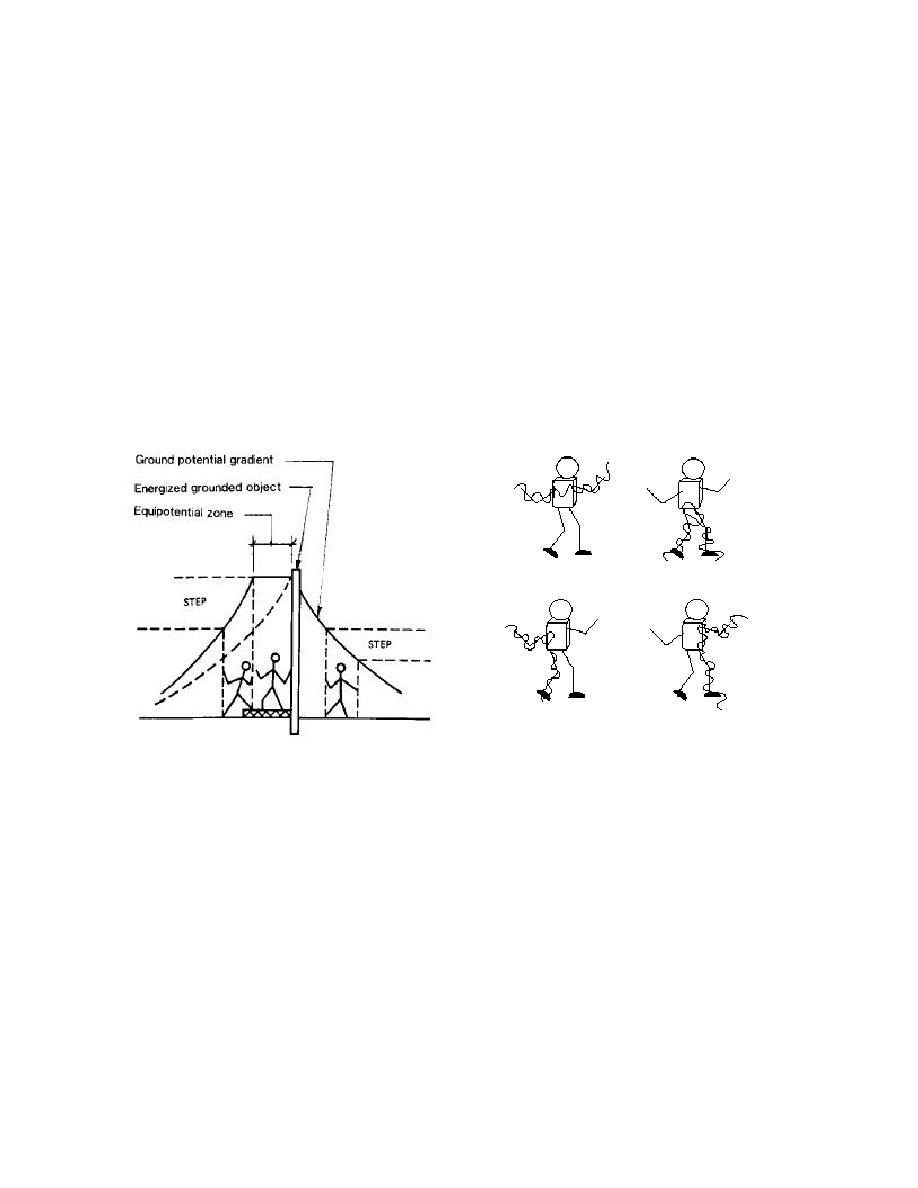
4.3.1 Dangers From Electric Shock. Electric shock results from setting up an electric
current path within the human body. The current flows because there is a potential gradient
(voltage difference) between an energized object and the grounded worker. Figure 1 shows
potential gradients and the safe area or equipotential zone, which has no potential gradient.
Figure 2 indicates current flow paths. Table 1 indicates the effects of 60-hertz current on humans.
Touch Potential
Step Potential
Touch/Step Potential
Touch/Step Potential
The current path will determine which tissues and
organs will be damaged or destroyed. The pathway is
differentiated into three groups: touch potential, step
potential, and touch/step potential.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Ground Potential Gradient
Current Path Flow
10



 Previous Page
Previous Page
