UFC 4-023-03
25 January 2005
F-3.1
Example Building.
Continuing with the building defined in the Tie Force example, the use of
bridging (Alternate Path) can be illustrated as an alternative to developing vertical tie
capacity across all vertical studs in vertical load bearing elements. The load carrying
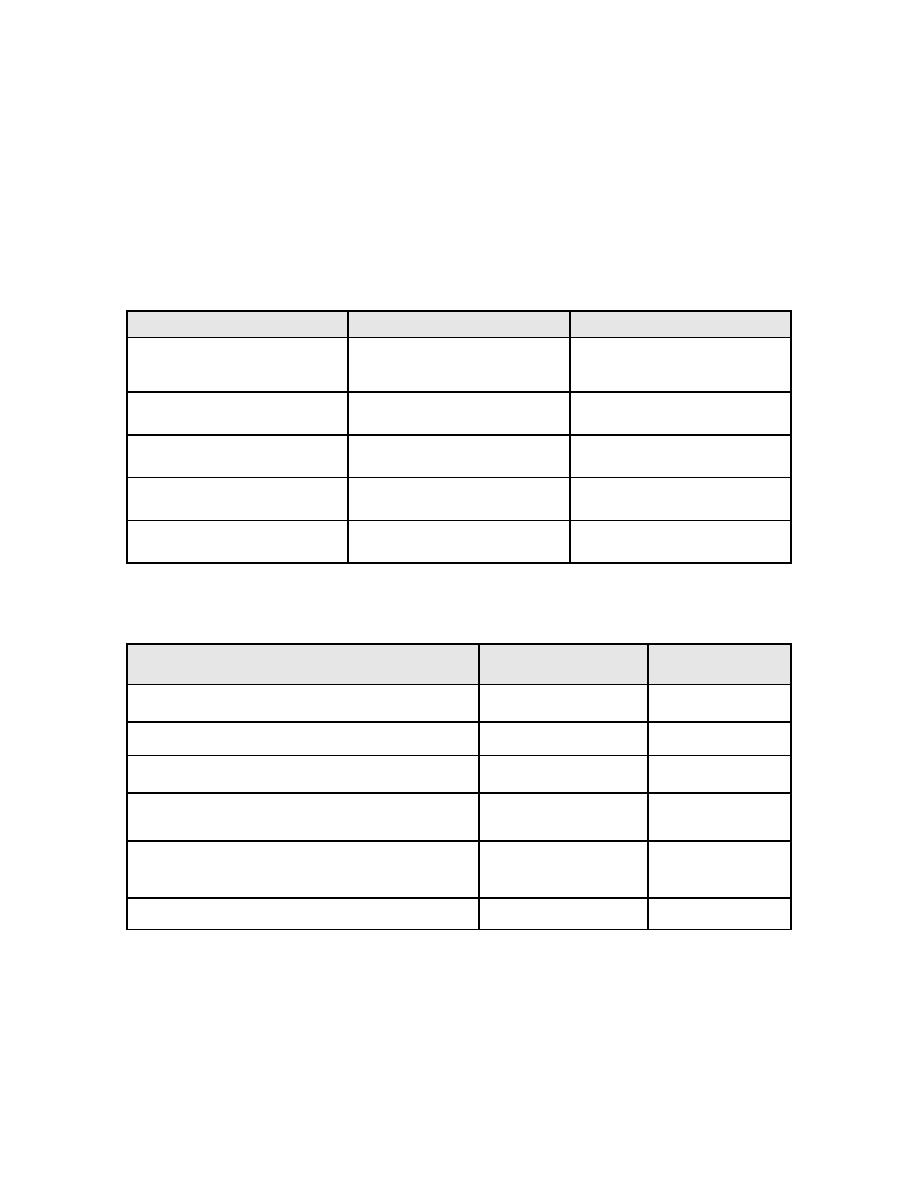
elements of the structure were defined previously and are summarized in Table F-3.
Table F-3 Load Carrying Elements
Element
Section
Material
Southern Yellow Pine
Walls (int and ext)
2x6 @ 16" 0.C.
(SYP) No. 2
Columns
4 2x6
SYP No. 2
Rim Beam
8x12
SYP No. 2
Girder
8x12
SYP No. 2
Floor Joists
11.9" engineered I-Joists
Engineered Wood
Loading was specified in the Tie Force example and is summarized in Table F-4.
Table F-4 Applied Loading (unfactored)
Level or Element
Dead
Live
Roof
20 psf
20 psf
3rd Floor
15 psf
55 psf
2nd Floor
15 psf
55 psf
Exterior wall section including sheathing
6.5 psf
Brick Cladding (supported at ground, 2nd ,
40 psf
and 3rd floor levels)
Rim Beam / Girder (est.)
25 plf
As specified in Section 3-2, the alternate path method is applied to each
deficient vertical load-carrying element. The rim beam and the wall section may be
used to bridge deficient vertical elements. For this structure, it is necessary to show
alternate paths for interior and exterior columns and load bearing walls. The facility is
being designed for a Low LOP. Only a portion of the elements will be illustrated in this
example.
F-11



 Previous Page
Previous Page
