DG 1110-3-106
b. For general guidance on interior design, see DG
(3) The laboratories shown are contained in the
1110-3-122.
standard classroom module, but any size that fits the
school's structural system may be used since these
G. Criteria.
are highly dedicated spaces. The standard laboratory
Table 4-2 lists outline criteria for designing laboratory
casework may be planned on the 5-foot-square grid.
classrooms.
When the nature of the work and length of the-class
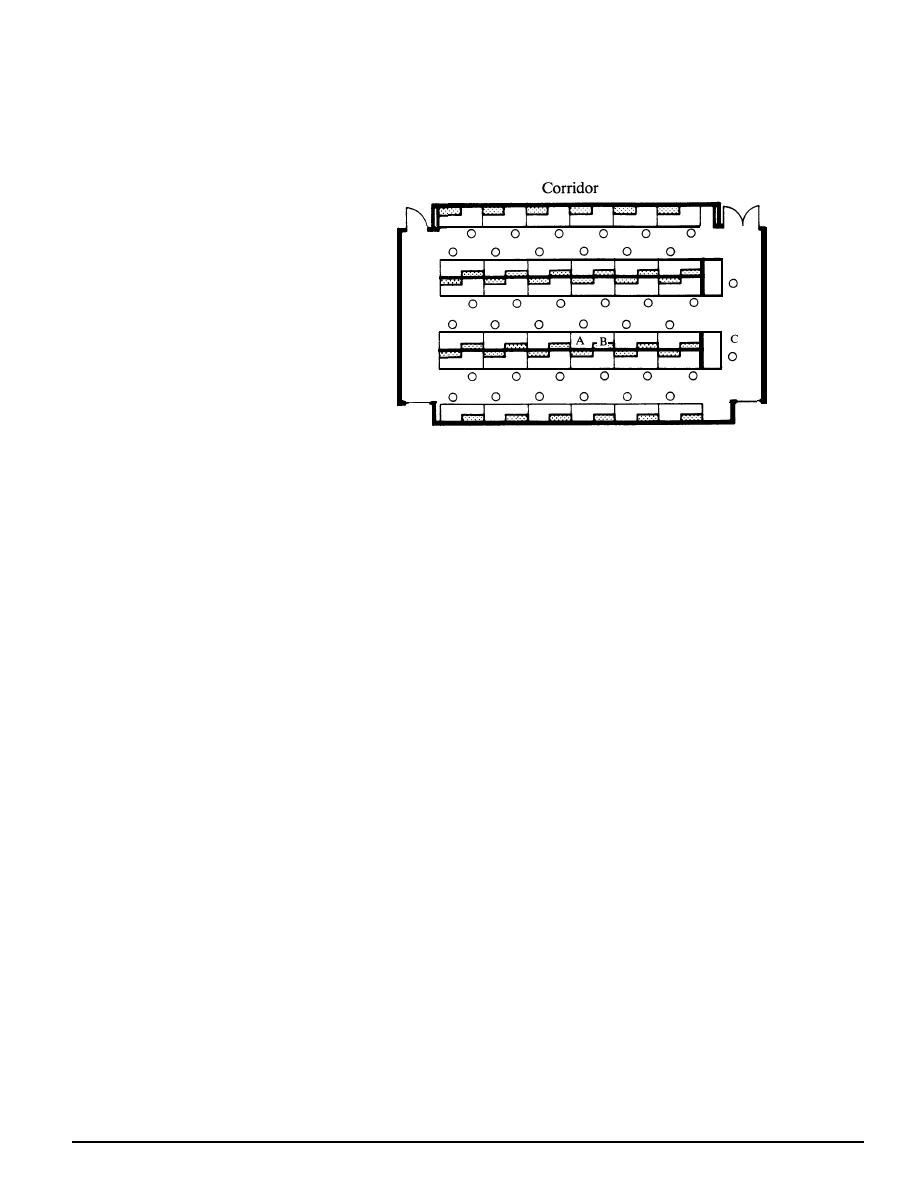
A Work Space
B Equipment
C Instructor
Figure 4-19
Laboratory Classroom for Standing Instruction.
4-4 Instructional Shops.
allow, a 10-foot spacing between the centerlines of
counters may be used for stand-up work. (Figure
A. Use/Activities.
4-19). When seats are required, a 15-foot spacing
Instructional shops and laboratory spaces are enclosed
should be used as shown in Figures 4-17 and 4-18.
spaces for conducting applied training in using and
maintaining Army equipment. Laboratories generally
E. Access/Circulation.
refer to spaces where equipment is small and a number
of similar workstations or work benches can be
(1) Location.
grouped into one room. Instructional shops generally
Laboratory classrooms should be clustered into suites
refer to spaces for larger equipment and vehicles;
containing space for apparatus storage, preparation of
students work in small groups or rotate among
demonstrations, and lectures. (Figure 4-20 and
specialized locations. Because of this diversity, this
paragraph 5-2 below).
guide cannot provide specific dimensional or loading
criteria for laboratories/shops. However, the planning
(2) Circulation.
factors below pertain to shop design at all service
Aisles should provide ease of movement between the
schools .
classroom and laboratory areas and around the
laboratory equipment. It should be possible to move
B. Occupants.
equipment in and out easily. Circulation in a
The instructor-student ratio will vary between 1:40 and
laboratory classroom must meet the same life-safety
1:20 or less.
criteria as classrooms. Special doors may be needed to
move laboratory equipment in or out of the room.
C. Equipment/Supplies.
Enough space should be provided around laboratory
Most instructional shops house U.S. Army equipment
equipment so students can see well and to insure that
for training use. Depending on the school, this
material movement does not create hazards.
equipment includes communication devices, computers,
wheeled vehicles, artillery pieces, tracked and armored
F. Interior Design.
vehicles, guided missiles, and fixed and rotary-wing
aircraft. Some shop areas house mockups instead of
(1) Recommendations:
actual U.S. Army equipment items. These devices
simulate, within a controlled environment, items of
a. For recommendations, see Figure 4-21. For color
inventory equipment, especially field equipment. They
schemes called out in the figure, see the Appendix.
are often made from parts of actual equipment and
are partially operable; for example, the Armor School
4-17



 Previous Page
Previous Page
