1110-3-106
Conference
Classrooms
Laboratory
Classrooms
Self-Paced
Classrooms
Computer Aided
Classrooms
Seminar
Classrooms
Auditorium/
Theater
Instructor Rehearsal
Rooms
Counseling
Rooms
Remedial Instruction
Rooms
Study Areas
Snack &Vending
Rooms
Student Lounge
Restrooms
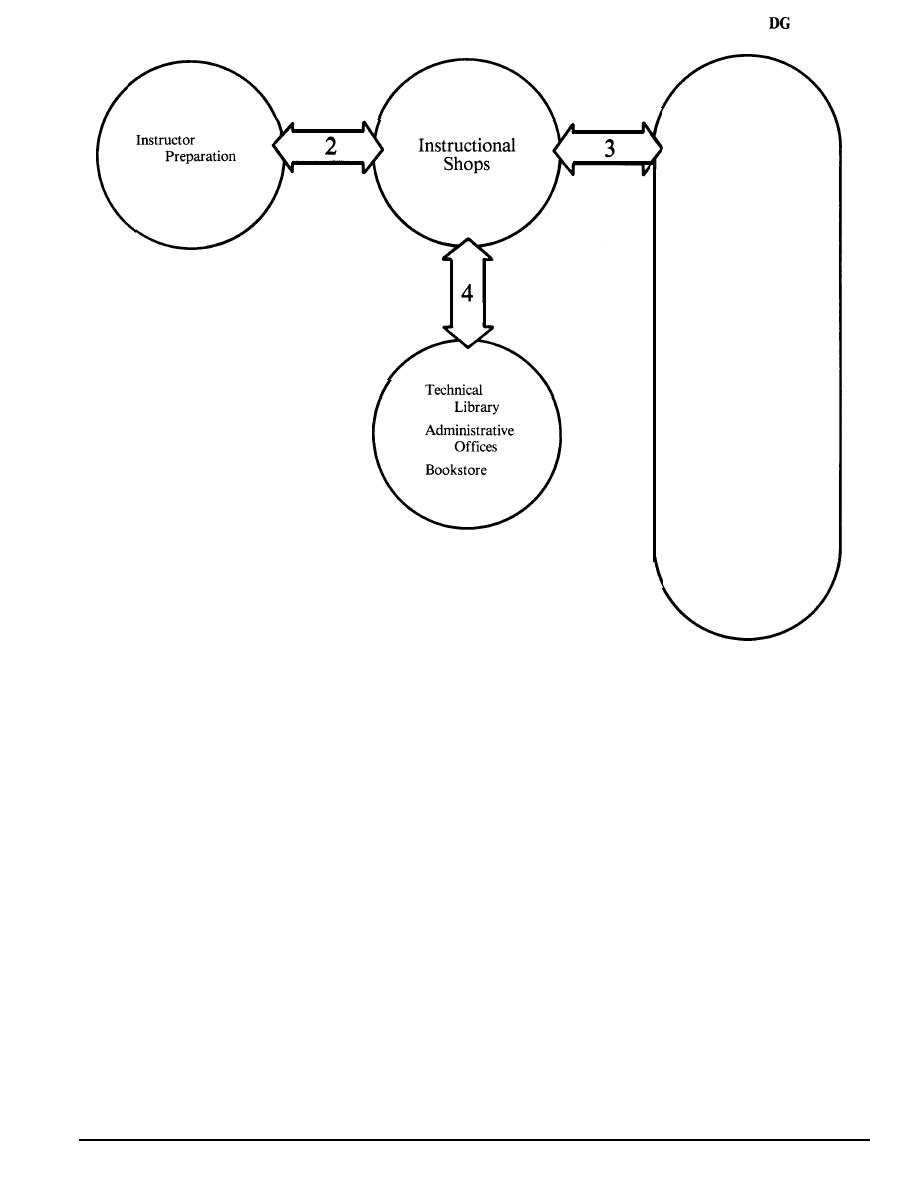
Figure 4-23
Spaces Near Instructional Shops.
c. General circulation among different spaces in the
(3) Openings and Access.
laboratory/shop should not disturb students who are
working. A corridor or circulation route with training
a. It should be easy to move equipment in and out of
spaces on each side will reduce disturbances. Routes
the laboratory/shop. Laboratories/shops which use
through training spaces should be avoided.
vehicles or large equipment (i.e., that will not fit
through a 3- or 6-foot-wide doorway) should have an
d. Floor systems should be designed to support
overhead or track-mounted door. The door should
expected heavy-equipment loads. When existing
allow direct entry to a shop from the outside.
facilities are changed for laboratory/shop use, floor
strength and other structural parts should be evaluated
b. A general circulation plan should be developed
by a structural engineer to determine their capacity.
when buildings are changed for laboratories and shops.
The advantages and disadvantages of outdoor and
G. Furniture.
indoor routes should be compared. Outdoor routes
Furniture should be durable and easy to clean.
require a drive and a door for each laboratory/shop
area. Indoor routes may create vehicle-pedestrian
H. Interior Design.
traffic hazards and will use up space within the
building; however, they will reduce the number of
(1) Finishes.
doors to the outside. Doors may increase energy use
Walls and floors should be durable and easy to clean.
and ventilation for the building, depending on climate,
Depending on laboratory/shop activities, surfaces may
laboratory/shop activities, and other factors.
4-23



 Previous Page
Previous Page
