TM 5-814-9
6.21 Waste oil storage
must be strategically located, easily accessible for servicing and
durable. Daily inspection of the oil skimmer unit is required to
Waste oil storage tanks are designed, constructed and installed
insure continuous, trouble-free operation.
in accordance with current U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency, State, or Local regulations for above ground or
6-23. Other considerations
underground storage tanks. Storage tanks should be 500- to
2000-gallon (1893- to 7570-liter) capacity, depending on the
Sediment basins should have pipe rail or fencing mounted on
estimated amount of oil recovery and frequency of cleanout.
the wall in accordance with OSHA requirements for safety
Positive spill containment should be provided at the cleanout
considerations; or the grade surrounding basins located lower
port and directed back to the sediment basin.
than top of wall to provide a safety barrier. Hydrostatic pressure
relief should be provided where generally high water tables
6-22. Maintenance
exist and basins should be designed to prevent flotation when
empty. Access ramps should be serrated for vehicle traction.
Routine maintenance of the sediment basin and appurtenances
Inlet and outlet ends should be readily accessible to operators,
will be minimal. Sediment should be removed from each cell at
through an access road around the basins. Lighting should be
least once per year. The waste oil storage tank should be
provided at the inlet structure and at the outlet structure.
emptied before its capacity has been reached. Provide appro-
priate site gauges and/or high level alarms. Oil skimmer devices
Section IV. SECONDARY TREATMENT
6-24. Onsite secondary treatment
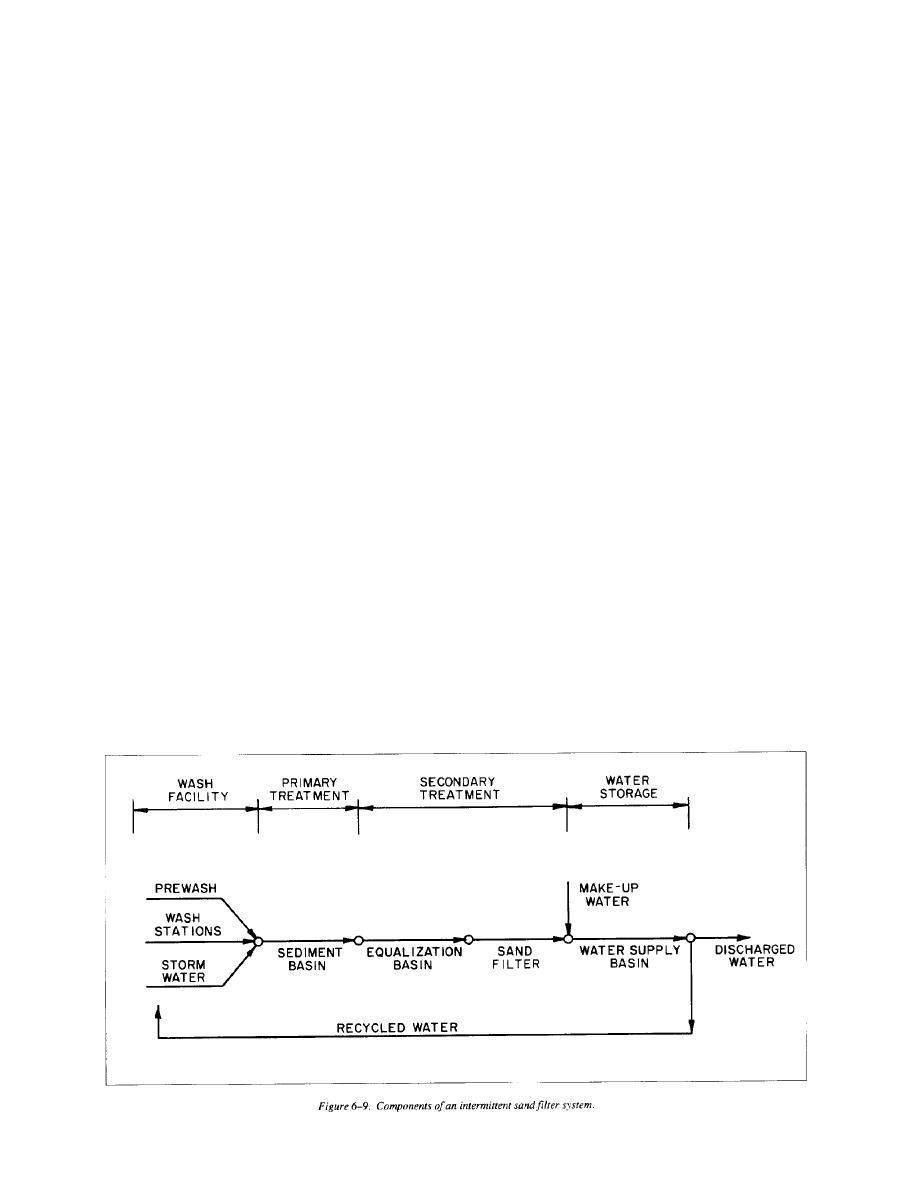
and series lagoons. Intermittent sand filter systems are the
preferred secondary treatment method for CVWFs. Where
At installations where an adequate, dependable, low-cost wash
existing ponds, lagoons, or basins are available and
water source cannot be found, and favorable site and weather
environmentally suitable for use, a lagoon system should be
conditions exist, a recycle water system should be used. The
considered. The most environmentally acceptable, cost-effective
water source must adequately supply clean water on demand
system should be used.
during the peak wash periods. The quality of effluent from a
sediment basin usually is not adequate for discharge to a sewage
6-25. Objective
treatment plant, even if treating non-cohesive soils and
therefore, cannot be used as recycled water. For recycling,
Secondary treatment removes suspended matter, microorgan-
secondary treatment is required. If an adequate water supply
isms, impurities, and minor residual oils from the product water.
source is available and recycling would not be economical, the
These materials are carryovers from the primary treatment
wastewater may be discharged to an existing sewage treatment
process and consist mostly of colloidal materials such as clays
plant for further treatment. In this case, onsite sediment basins
and fines that have not been removed during sedimentation. The
followed by an equalization basin would still need to be
removal of these suspended solids is essential to produce a
provided. Two altemative onsite secondary treatment systems
relatively clean, clear, acceptable product for recycling as wash
are available for treating waste washwater to a quality suitable
water.
for reuse in vehicle washing, namely, intermittent sand filtration
6-12



 Previous Page
Previous Page
