TM 5-805-4/AFJMAN 32-1090
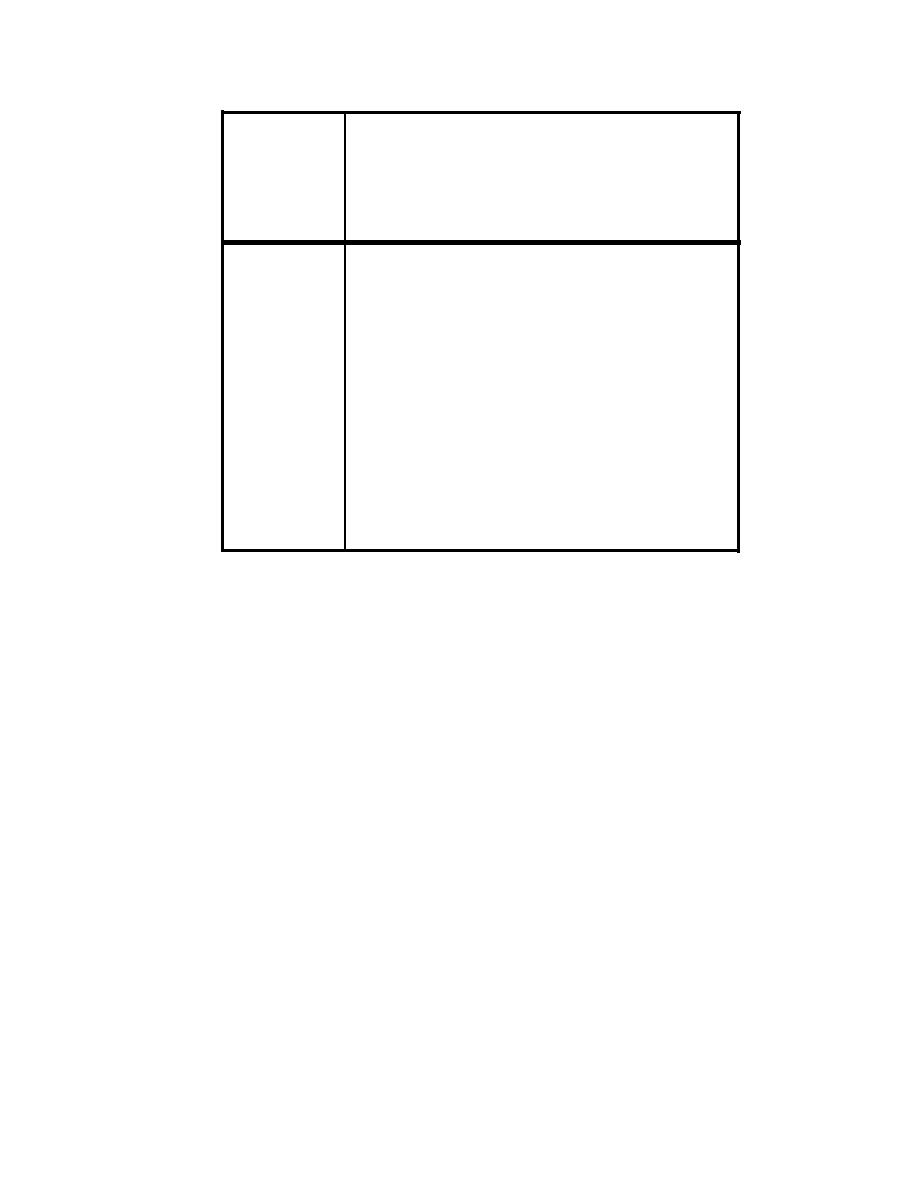
Table 4-7. Transmission Loss (in dB) of Plywood, Lumber, and Simple Wood Doors.
Thickness of Plywood or Lumber (in.)
2
4
Octave
1/4
1/2
1
Approximate Surface Weight (lb/ft.2)
Band
8
16
(Hz)
1
2
4
12
17
31
0
2
7
17
18
63
2
7
12
18
19
125
7
12
17
19
22
12
17
18
250
22
30
500
17
18
19
30
35
1000
18
19
22
35
39
2000
19
22
30
43
4000
22
30
35
39
43
47
8000
30
35
39
28
33
STC
18
21
24
Notes:
Surface weight based on 48 lb/ft.3 density, or 4 lb/ft.2 per in. thickness.
1.
2. Lumber construction requires tongue-and-groove Joints, overlapping joints,
or sealing of joints against air leakage. For intermediate thicknesses,
interpolate between thicknesses given in table.
3. For ungasketed hollow-core flush-mounted wood doors, use TL for l/h-in.
thick plywood.
4. For solid-core wood doors or approximately 2-in. thickness, well gasketed
all around, use TL for 2-in. thick plywood.
5. For small-area doors or boxes, framing around Cage of panel adds effec-
tive mass and stiffness and will probably give higher TL values than shown.
(a) Support of floating floor. The floating
can be added to any one of the Type 1 through 4
combinations. This becomes necessary when all
concrete floor should be supported off the structure
o t h e r floor systems clearly fail to meet the
floor at a height of at least 2 inches with properly
required TL values. The values given in table
spaced blocks of compressed glass fiber or multiple
4-16 are improvements in TL that can be added
layers of ribbed or waffle-pattern neoprene pads or
to the values of tables 4-12 through 4-15 if a
steel springs in series with two layers of ribbed or
well-designed and well-constructed floating floor
waffle-pattern neoprene pads. The density and
is used. Where careful designs have included
loading of the compressed glass fiber or neoprene
prevention of flanking paths of sound or vibra-
pads should follow the manufacturers' recommen-
dations. If steel springs are used, their static
tion, the table 4-16 values have been achieved
and even exceeded. However, if flanking paths
deflection should not be less than 1/4 inch. In some
systems the 2-inch space between the floating slab
are not prevented by intentional design consider-
ations, only one-half of these improvements may
and the structure slab is partially filled with a
be reached.
1-inch thickness of low-cost glass fiber or mineral
4-13



 Previous Page
Previous Page
