UFC 3 -520-01
June 10, 2002
C-2
Determining Capacitor Size.
C-2.1
Determine the required capacitor size to improve power factor in accordance
with the following expression:
kVARcap = kW (tan θ1 - tan θ 2 )
where,
kVARcap
= Required capacitor size in kVARs
kW
= Active power in circuit
?1
= Phase angle before applying power factor correction
?2
= Desired phase angle after power factor correction
C-2.2
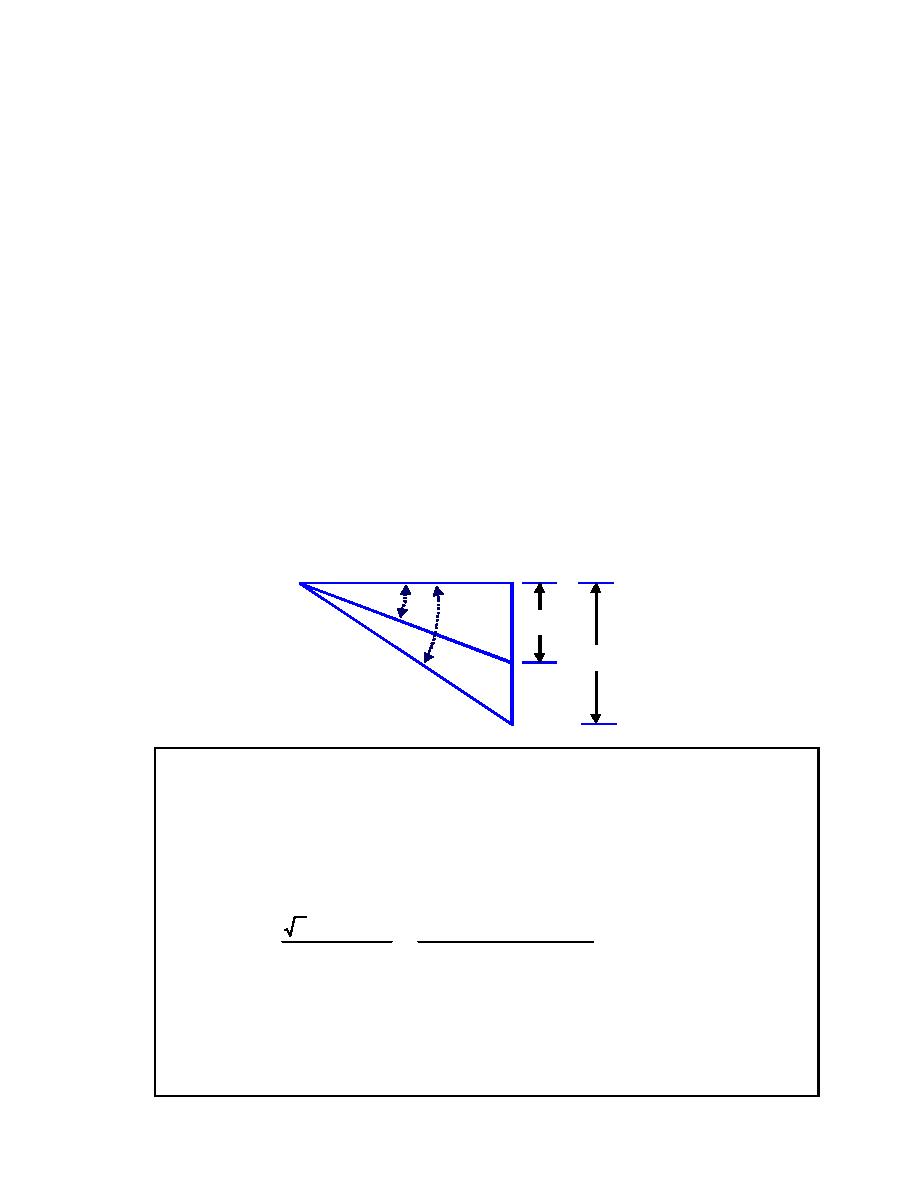
Figure C-2 shows the phasor relationship for power factor correction. The
addition of kVARs by a shunt capacitor reduces the supplied kVAR.
Figure C -2. Phasor Diagram for Power Factor Correction
kW
θ2
θ1
kVAR2
kVA
2
kVAR1
kV
A
1
EXAMPLE: A three-phase, 460-volt, 50 horsepower (37,300 watts) motor has a
power factor of 0.65. What capacitor rating is needed to improve the power
factor to 0.95?
First, calculate the power required by the motor at full -load conditions. NEC
Table 430.150 (2002 Edition) specifies a typical full -load current of 65 amperes.
The load power is then calculated by:
3 V I pf
1.73 460 65 0.65
P (kW ) =
=
= 33.7 kW
1000
1000
For a power factor of 0.65, cos ?1 = 0.65, or ?1 = 49.46, and tan ?1 = 1.17. The
desired power factor is 0.95, or ?2 = 18.19, and tan ?2 = 0.33. The required
capacitor size is given by:
kVARcap = kW (tan θ 1 - tan θ 2 ) = 33.7 (1.17 - 0.33) = 28.3 kVAR
C-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
