UFC 3-530-01
22 August 2006
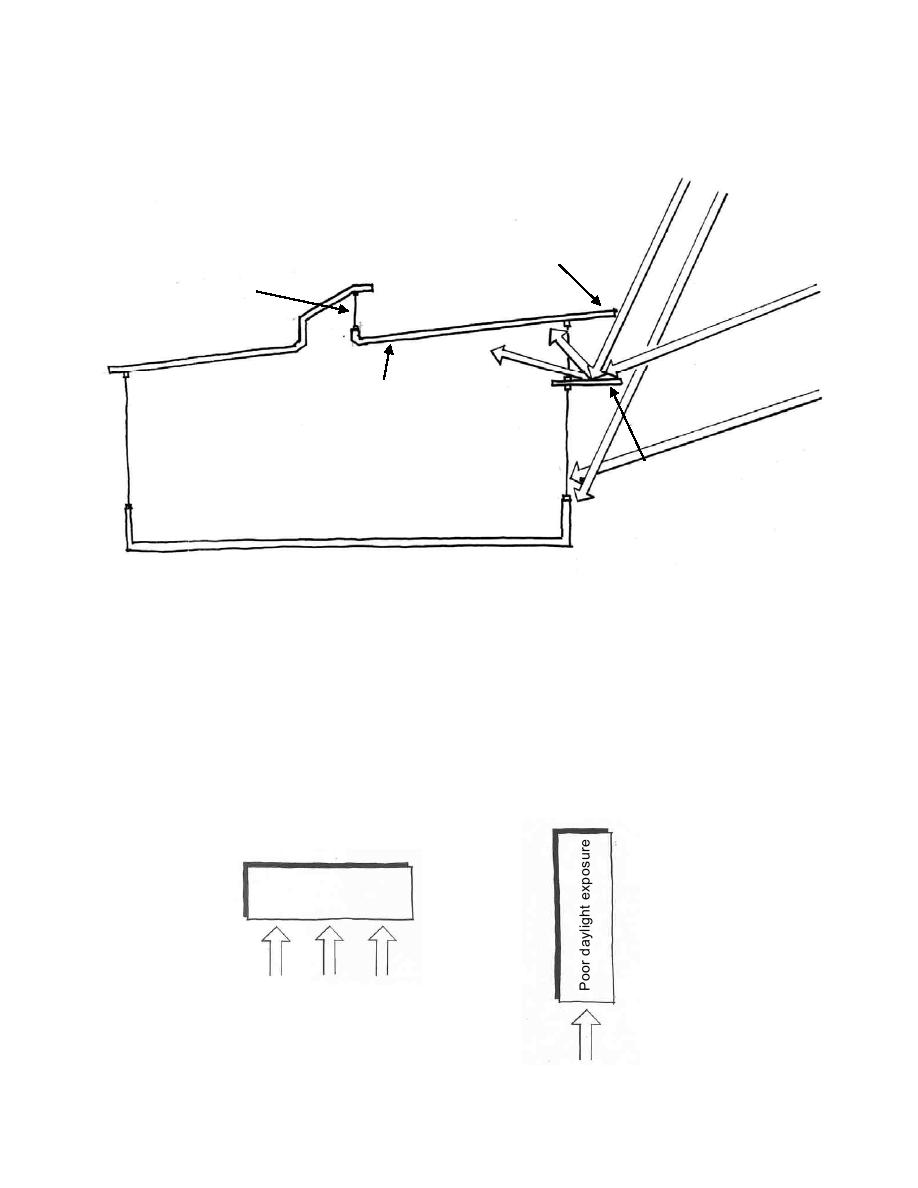
Figure 4-1. Examples of daylighting Strategies.
High Summer
Sun Angle
Vertical glass is
shaded by overhang
on south side.
Toplighting for
interior of the space.
Low Winter
Sun Angle
Slope ceiling to increase
ceiling brightness.
No overhang required
on north side.
Low angle sunlight allows
Lightshelf reflects
thermal gain, but also
light onto ceiling
introduces potential for
and shades view
direct glare.
windows.
4-6
GLAZING ORIENTATION. Building orientation is critical to maximizing
daylight potential. North- and south-facing buildings provide the most effective
orientations while East- and West-facing buildings may allow excessive heat gain and
are hard to control direct sun penetration. South orientations have the potential of
providing over 50% of the daylight. The success to daylighting with south orientations is
controlling the direct sunlight penetration with shading devices. North orientations
require minimal shading in the winter months. East and West orientations require
manual shading devices. Vertical blinds control daylight well on this orientation.
Figure 4-2. Building orientation can maximize daylight exposure.
NORTH
NORTH
Good daylight exposure
SOUTH
SOUTH
4-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
