TM 5-811-7
electrolyte), a continuous electrolyte from the
zinc because of these metals' higher potential
anode to the protected structure, and an external
compared to steel structures.
b. Impressed current systems. Impressed current
metallic connection (wire). These items are
essential for all cathodic protection systems.
cathodic protection systems use the same elements
as the galvanic protection system, only the
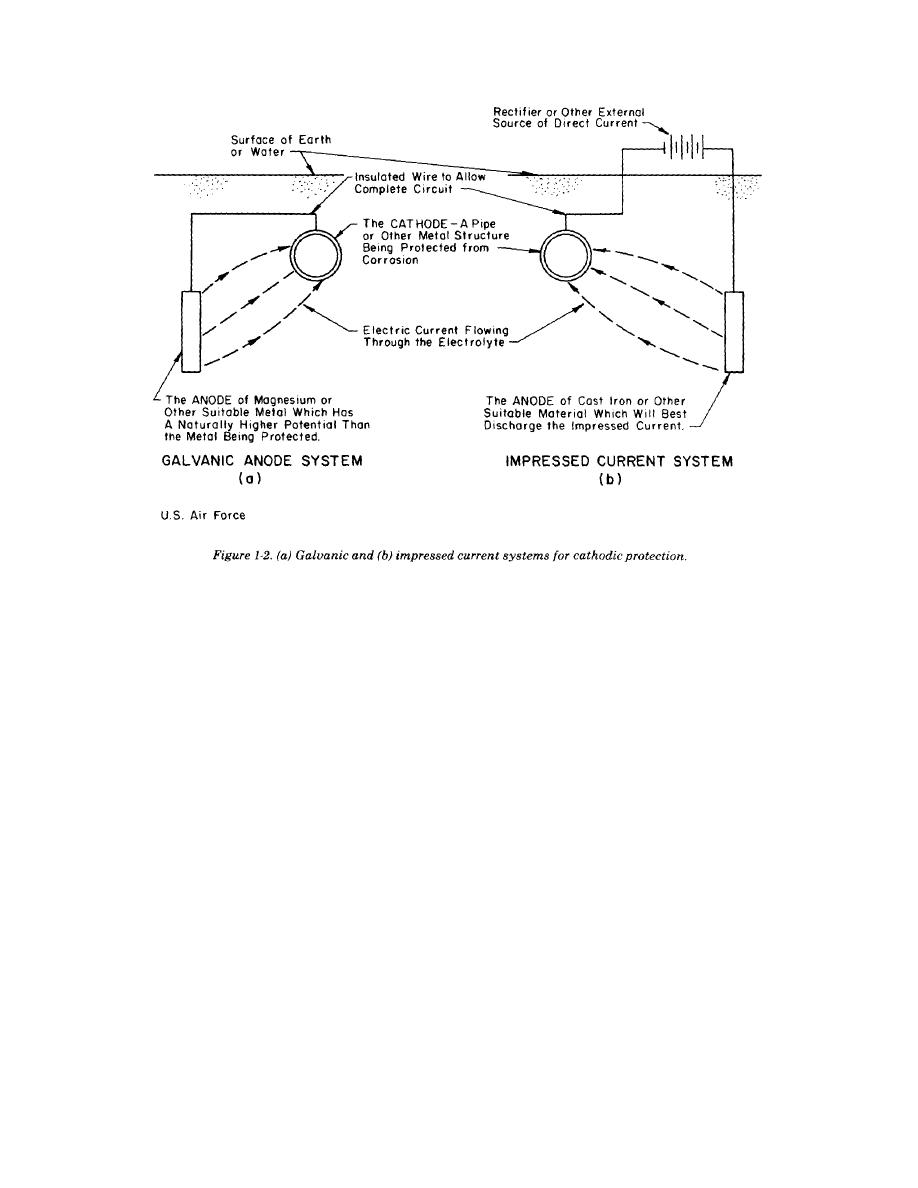
a. Galvanic system. A galvanic cathodic pro-
structure is protected by applying a current to it
tection system makes use of the corrosive poten-
from an anode. The anode and the structure are
tials for different metals. Without cathodic protec-
connected by an insulated wire, as for the galvanic
tion, one area of the structure exists at a more
system. Current flows from the anode through the
negative potential than another, and corrosion
electrolyte onto the structure, just as in the galvanic
results. If, however, a much less inert object (that
system. The main difference between galvanic and
is, with much more negative potential, such as a
impressed current systems is that the galvanic
magnesium anode) is placed adjacent to the struc-
system relies on the difference in potential between
ture to be protected, such as a pipeline, and a
the anode and structure, whereas the impressed
metallic connection (insulated wire) is installed
current system uses an external power source to
between the object and the structure, the object will
drive the current, as figure 1-2b shows. The
become the anode and the entire structure will
external power source is usually a rectifier that
become the cathode. That is, the new object cor-
changes input a.c. power to the proper d.c. power
rodes sacrificially to protect the structure as shown
level. The rectifier can be adjusted, so that proper
in figure 1-2. Thus, the galvanic cathodic protec-
output can be maintained during the system's life.
tion system is called a sacrificial anode cathodic
Impressed current cathodic protection system
protection system because the anode corrodes
anodes typically are high-silicon cast iron or
sacrificially to protect the structure. Galvanic
graphite.
anodes are usually made of either magnesium or
1-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
