TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
13-4.
Fluidized bed performance
predicted nitrogen oxide emissions.
e. Several fluidized bed boiler manufacturers are
a. With the exception of a baghouse or precipitator,
now offering performance guarantees based upon
which is required for particulate removal, additional
experience in the bubbling, circulating, and dual bed
gas cleaning devices are not required for environmental
designs.
control with fluidized bed systems.
b. Fluidized bed boilers are able to remove sulfur
13-5.
Materials and construction
dioxide directly in the combustor. This is accomplished
by using limestone in the fluid bed. The limestone
The materials used for construction of fluidized bed
calcines to form calcium oxide (CaO) and then reacts
units are similar to those used in conventional boilers
with SO2 to form calcium sulfate as follows:
depending on the design pressure and temperature of
the system.
in-bed tubes have experienced high erosion rates in
some cases. Vertically oriented tubes are less prone to
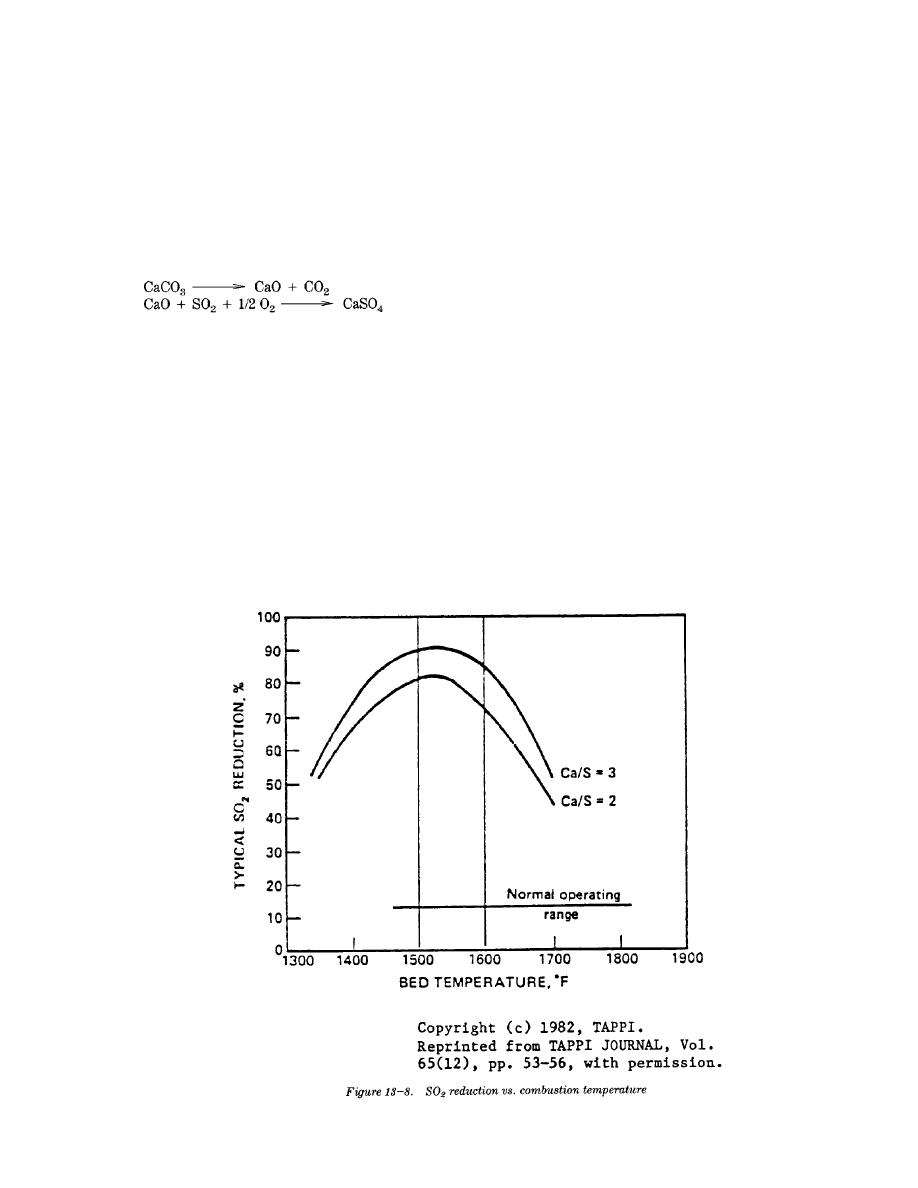
The ideal temperature range for desulfurization in a
erosion than the horizontal ones. Where in-bed tubes
fluidized bed is about 1600 degrees Fahrenheit.
are used, consideration should be given to use of
c. A bubbling fluidized bed boiler will require a
thicker walls on the tubes and their metallurgy. Wear
higher calcium to sulfur ratio for control of SO2, while
fins can be installed to reduce erosion. Also, some
the circulating fluidized bed boiler can achieve similar
corrosion may be experienced due to the reducing
SO2 removal with the Ca/S ratio of 1.5 to 2. See figure
atmosphere in the lower regions.
b. Fluidized bed. The fluidized bed or bottom of the
13-8.
d. Nitrogen oxide is controlled by distribution of
combustor section varies considerably with each type
primary air under the bed and secondary air part way
of design. The method used for air distribution is
up the combustor. The staging of combustion limits the
important in maintaining uniform fluidization across
nitrogen oxide to that which is formed only by fuel-
the bed. Some units have had problems with plugging
bound nitrogen. Thermally formed nitrogen oxide is
of the air openings. The bottom is castable refractory-
negligible in the fluidized bed. See figure 13-9 for
lined on some units. Others have heat transfer tubes
13-8



 Previous Page
Previous Page
