UFC 3-440-01
14 June 2002
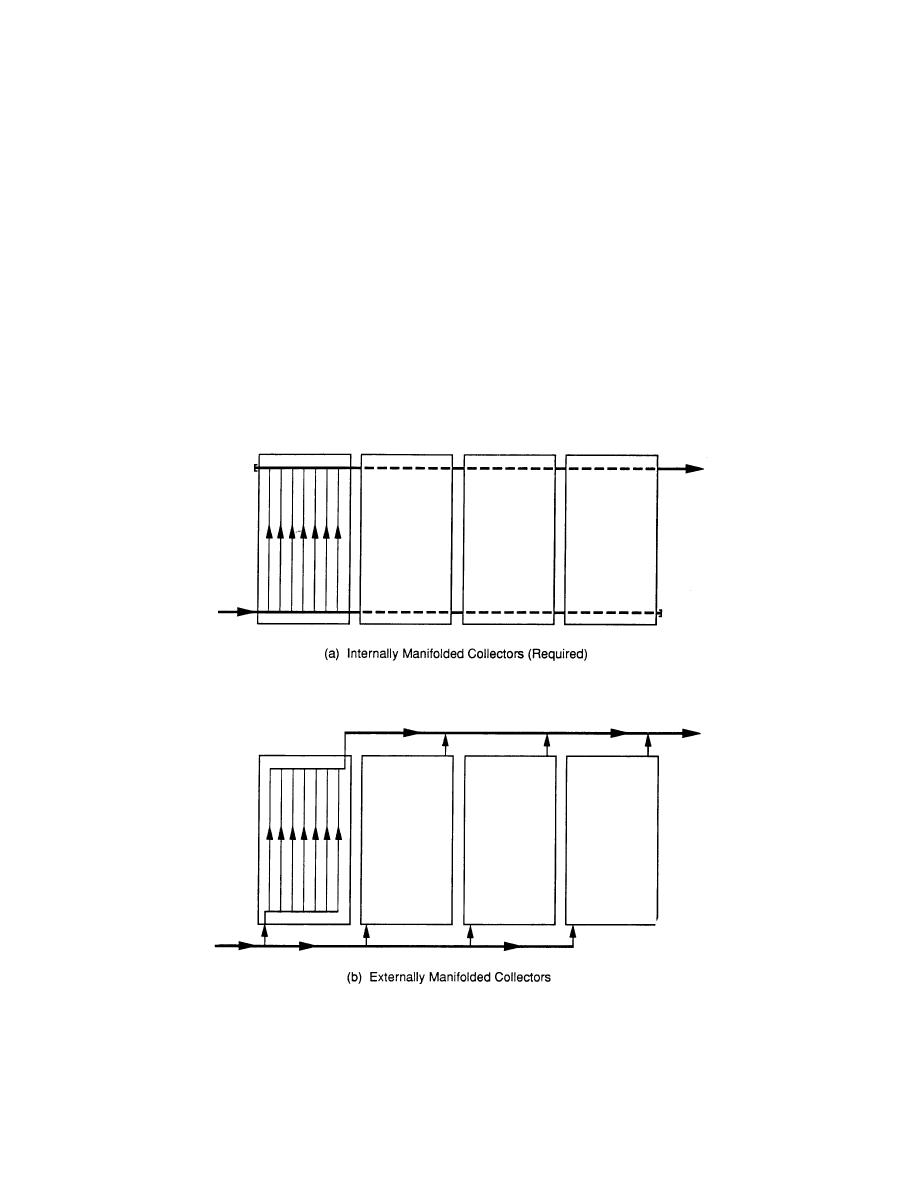
from the array supply to each of the individual collectors. There are two main types of
collector manifolds: external and internal. External-manifold collectors have small
diameter inlets and outlets that are meant to carry the flow for only one collector. The
manifold piping to each inlet and from each outlet remains external to the collector.
Today, external-manifold collectors are being replaced by those with internal manifolds.
Internal-manifold collectors have larger manifolds designed to carry the flow for many
collectors connected together, with the manifolds built into the collector unit. Figure 4-1
shows an example of both types of manifold collectors. The internal-manifold collector
has many advantages, particularly when used in large systems. Benefits include
reduced costs for piping materials, pipe supports, insulation, and labor; more effective
flow balancing, which improves thermal performance; and the reduced heat losses to
ambient air. Use internally manifolded collectors for all new design projects (externally
manifolded collectors will not be used).
Figure 4-1. Collector Manifold Types
4.2.1.1.4
Collector Glazings. Collector covers, or glazings, are required to let
radiant energy from the sun through to the absorber and to prevent convection from the
hot absorber plate to the ambient air. Some properties to consider when choosing
glazings are structural integrity and strength, durability, performance and safety.
4-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
