TM
S-805-4lAFJMAN
32-1090
factors influence the SPL in a receiving room: the
transmission loss of the composite wall (TLc) can
be calculated. The transmission coefficient "t", of
TL of the wall, the area SW of the common wall
each construction, is the ratio of the transmitted
between the source and receiving rooms, and the
acoustic power to the incident acoustic power and
Room Constant R2 of the receiving room. These
is related to TL by equations 4-5.
three factors are combined in equation 4-1:
t = 1/(10(0.1 x TL))
(eq 4-5)
Lp2 = Lp1 - TL + 10 log (1/4 + SW/R2)
(eq 4-l)
Once the transmission coefficient of each of the
were Lp1 is the SPL near the wall in the source
individual constructions has been determined then
room, and Lp2 is the estimated SPL in the receiv-
the composite transmission loss can be determined
ing room at a distance from the wall approxi-
by equation 4-6.
mately equal to 75 percent of the smaller dimen-
TLc = 10 log [S1 + S2 + S3+ . . . )/(S1t1 + S2t2
sion (length or height) of the wall. The "noise
+ S3t3 + . . . )]
(eq 4-6)
reduction" (NR) of a wall is the difference between
Lp1 and Lp2; therefore,
Where S1 is the surface area of the basic wall
NR + TL - 10 log (1/4 + SW/R2)
having transmission loss TL1, S2 is the surface
(eq 4-2)
=TL+C
area of a second section (such as a door) having
TL2, S3 is the surface area of a third section (such
where
as a window) having TL3, and so on. Since the
c = -10 log (1/4 + SW/R2)
(eq 4-3)
transmission loss is different depending on the
In the manual, C is called the "wall correction
frequency, this calculation must be repeated for
term" and its value is given in table 4-1 for a
each octave band of interest.
range of values of the ratio SW/R2. Both SW and R2
d. "Sound transmission class" (STC). Current
are expressed in ft2, so the ratio is dimensionless.
architectural acoustics literature refers to the term
When NR is known for the particular wall and
"Sound Transmission Class" (STC). This is a one-
room geometry, equation 4-1 becomes
number weighting of transmission losses at many
Lp2 + Lp1 - NR
(eq 4-4)
frequencies. The STC rating is used to rate parti-
The SPL at any distance from the wall of the
tions, doors, windows, and other acoustic dividers
receiving room can be determined by using figure
in terms of their relative ability to provide privacy
3-1, and extrapolating from the "starting dis-
against intrusion of speech or similar type sounds.
tance" (75 percent of the smaller dimension of the
T h i s one-number rating system is heavily
wall) to any other desired distance for the particu-
weighted in the 500- to 2000-Hz frequency region.
lar R2 value.
Its use is not recommended for mechanical equip-
c. TLc of composite structures. When a wall is
ment noise, whose principal intruding frequencies
made up of two or more different constructions,
are lower than the 500- to 2000 Hz region. How-
each with its own set of TL values, the effective
ever, manufacturers who quote STC ratings should
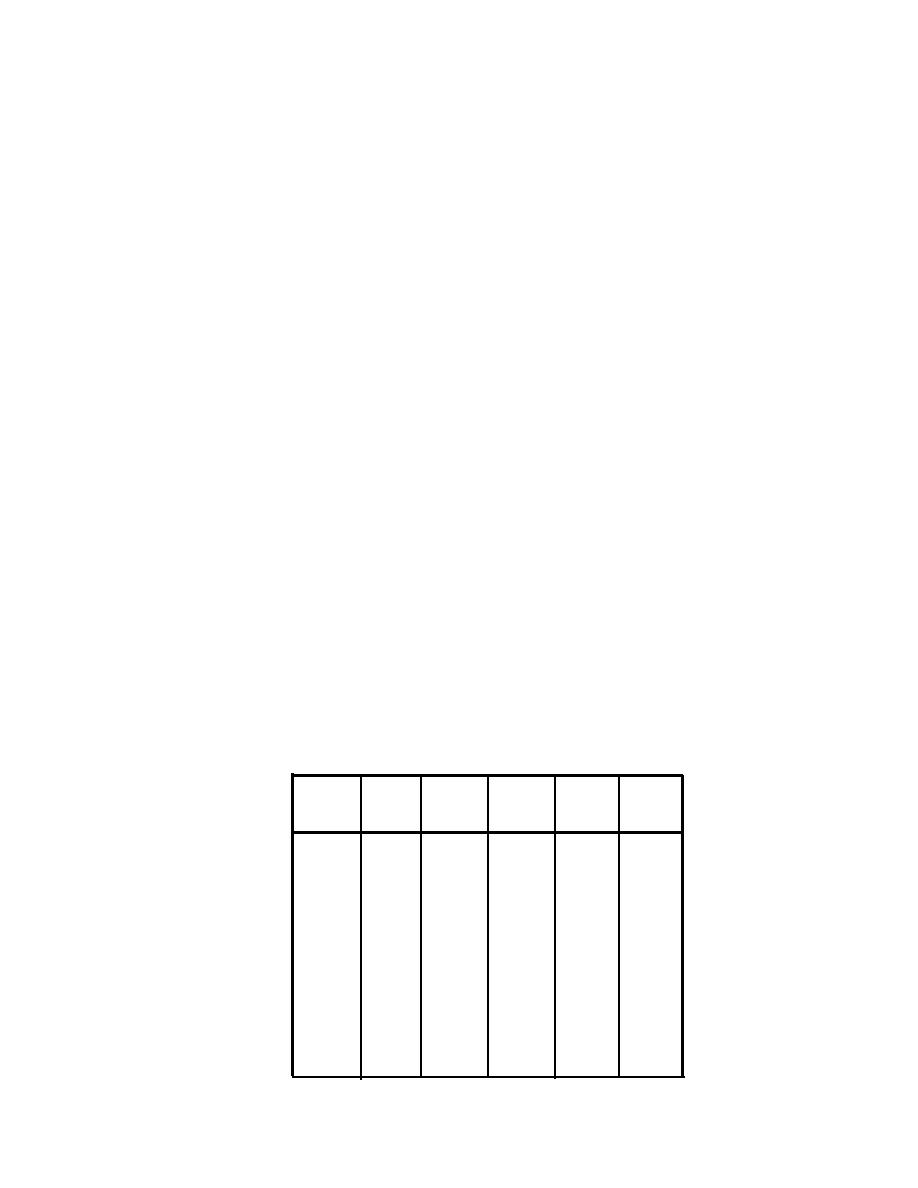
Table 4-1. Wall or Floor Correction Term "C" for Use in the Equation NR = TL + "C".
(Select nearest integral value of C)
Ratio
"C"
Ratio
"C"
Ratio
"C"
(dB)
(dB)
SW/R2
(dB)
SW/R2
SW/R2
0.00
+6
-12
1.7
-3
15
0.07
-4
2.2
20
+5
-13
+4
0.15
-14
-5
25
2.9
0.25
-6
+3
3.7
31
-15
0.38
+2
40
4.7
-7
-16
0.54
+1
-8
6.1
-17
50
0
0.75
7.7
-18
63
-9
1.0
-1
80
-10
9.7
-19
-2
12.0
1.3
-11
100
-29
4-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
