TM 5-805-4/AFJMAN 32-1090
have the 1/3 octave band TL data from which the
and the air in the cavity have natural frequencies,
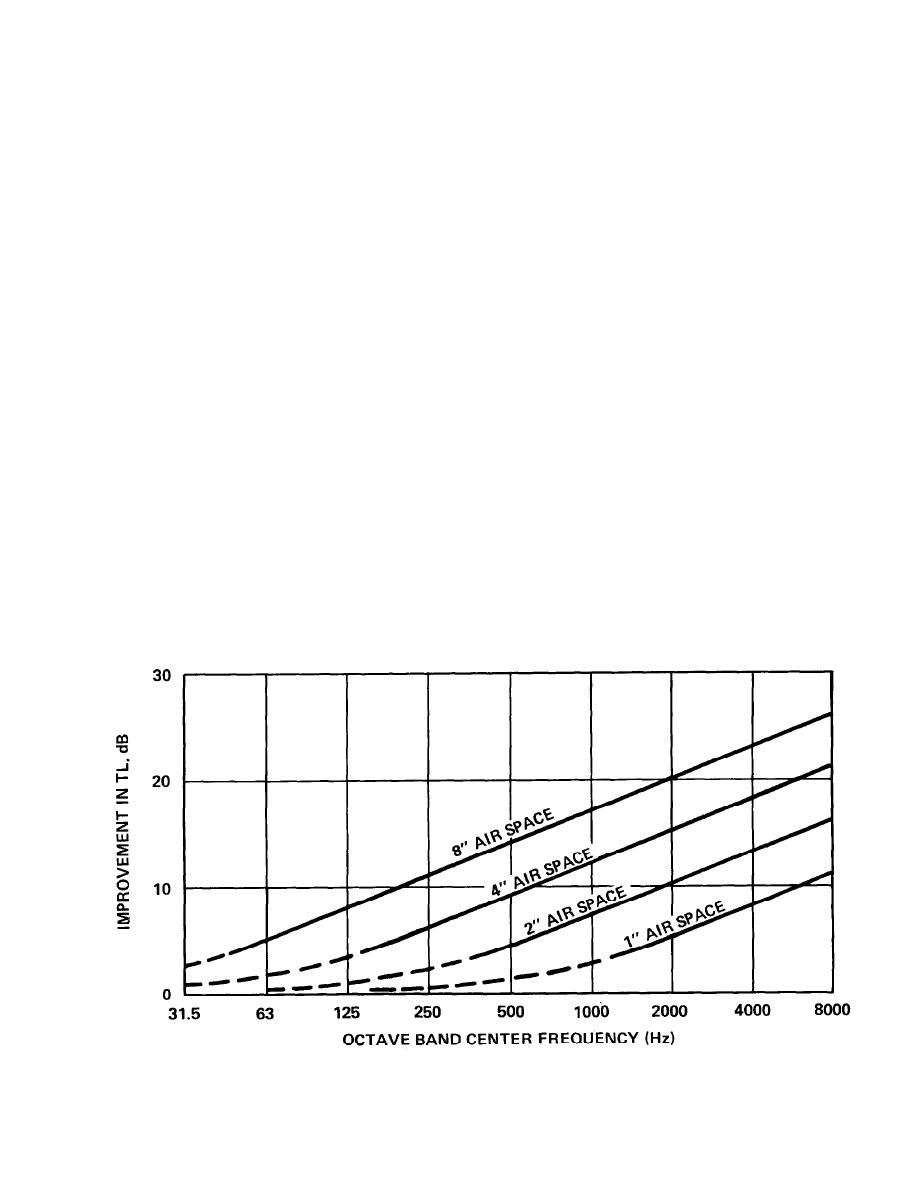
as seen in figure 4-2. The total effect of a double
STC values were derived, so it is possible to
wall, then, is to gain the improvement of figure
request the TL data when these types of partitions
4-1 but to lose some of that gain in the vicinity of
are being considered for isolation of mechanical
the natural frequency determined in figure 4-2. It
equipment noise. The procedure for determining
is suggested that a loss of 5 dB be assigned to the
an STC rating is given in ASTM standard E 413.
octave band containing the natural frequency and
e. TL of double walls. If mechanical equipment
a loss of 2 dB be assigned to the octave band on
rooms are bordered by work spaces where a moder-
each side of the band containing the natural
ate amount of noise is acceptable (such as areas of
frequency.
categories 5 and 6 and possibly in some cases
(2) Flanking paths. An obvious extension of
category 4 of table 2-2), the equipment noise
the double wall concept is a wide corridor used to
usually can be adequately contained by a single
separate a noisy mechanical equipment room and
wall. Double walls of masonry, or two separate
a category 2-4 area (table 2-2). Although the
drywall systems, can be used to achieve even
airborne sound path through the double wall may
greater values of TL. Various intentional and
appear to be under control, "flanking paths" may
unintentional structural connections between dou-
limit the actual achievable noise reduction into
ble walls have highly varying effects on the TL of
the quiet room. Figure 4-3 illustrates flanking
double walls. The improvement will be greatest at
paths. When a structure, such as a wall or floor
high frequency. The air space between the walls
slab, is set into vibration by airborne sound excita-
should be as large as possible to enhance the
tion, that vibration is transmitted throughout all
low-frequency improvement.
nearby connecting structures with very little decay
(1) Influence of air space. Figure 4-1 shows
as a function of distance. In a very quiet room,
the influence of the air space in double wall
that vibration can radiate as audible sound. For
construction, assuming no structural connections
most single walls between noisy and quiet spaces
between the two walls. Actually even though there
(part A of figure 4-3), the sound levels in the quiet
may exist no structural connection between the
room are limited by the TL of the single wall (path
walls, the walls are coupled by the intervening air
1), and the sound by the flanking path (path 2) is
space at low frequencies. The air space in a
too low to be of concern. However, the higher TL
double-wall cavity acts somewhat as a spring (air
of the double wall (part B of figure 4-3) reduces
is an "elastic medium"), and the mass of the walls
the airborne sound (path 1) so much that the
Figure 4-1. Improvement in Transmission Loss Caused by Air Space Between Double Walls Compared to Single Wall of Equal
Total Weight, Assuming no Rigid Ties Between Walls.
4-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
