TM 5-805-4/AFJMAN 32-1090
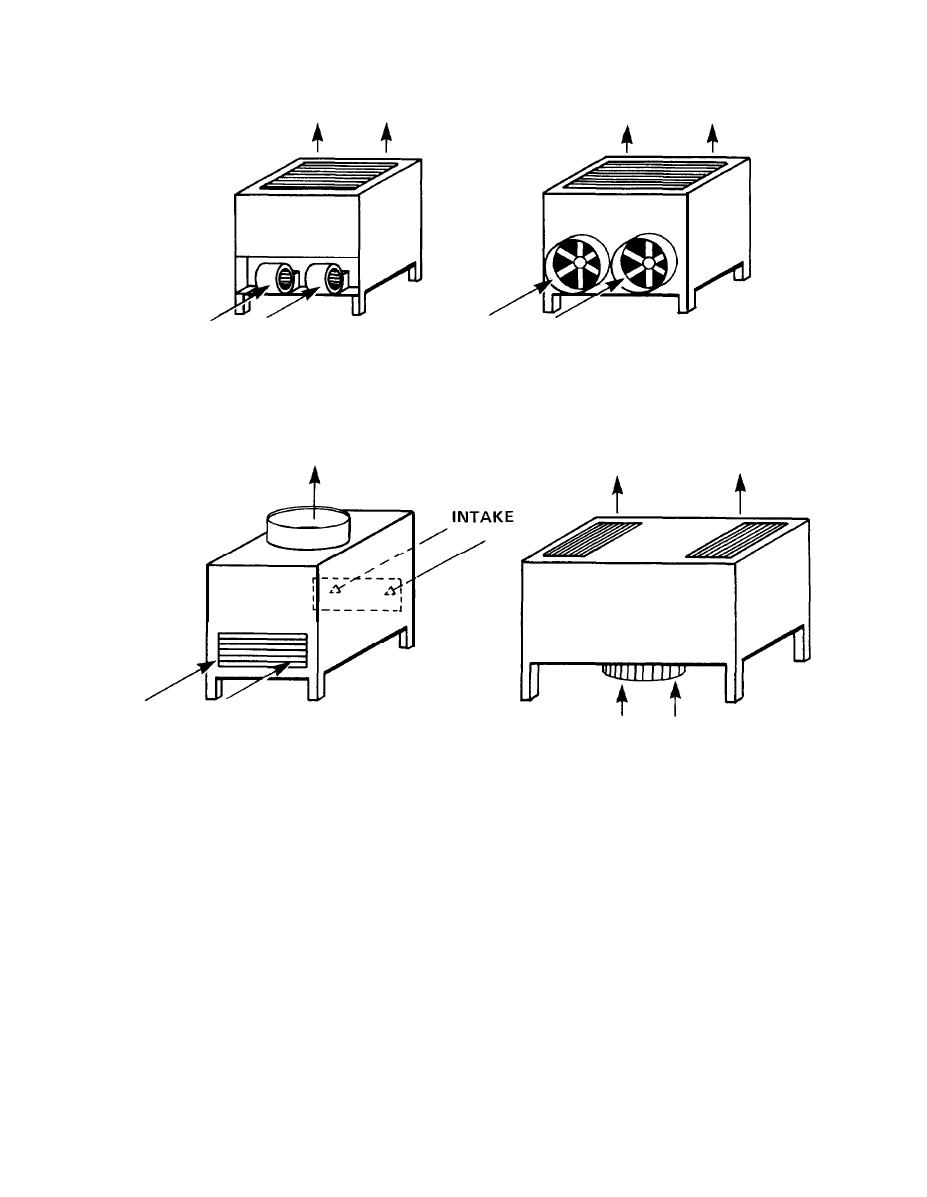
DISCHARGE
DISCHARGE
INTAKE
INTAKE
A. CENTRIFUGAL - FAN
B. AXIAL - FLOW
BLOW-THROUGH TYPE
BLOW-THROUGH TYPE
DISCHARGE
DISCHARGE
INTAKE
INTAKE
C. INDUCED - DRAFT
D. FORCED - DRAFT PROPELLER -TYPE
PROPELLER -TYPE
"UNDERFLOW"
Figure C-3. Principal Types of Cooling Towers.
centrifugal-fan cooling towers are given by equa-
tables 8-3 or 8-4. Cooling towers usually radiate
tions C-3 and C-4, respectively: for overall PWL
different amounts of sound in different directions,
(centrifugal-fan),
and the directional corrections of table C-9 should
be made to the average SPL. These corrections
Lw = 85 + 10 log (fan hp)
(eq C-3)
apply to the five principal directions from a cool-
for A-weighted PWL,
ing tower, i.e., in a direction perpendicular to each
LWa = 78 + 10 log (fan hp).
(eq C-4)
of the four sides and to the top of the tower. If it is
When more than one fan or cooling tower is used,
necessary to estimate the SPL at some direction
"fan hp" should be the total motor-drive hp of all
other than the principal directions, it is common
fans or towers. Octave band PWLs can be obtained
practice to interpolate between the values given
by subtracting the values of table C-8 from the
for the principal directions.
overall PWL.
c. Close-in SPLs. Sound power level data usu-
b. SPLs at a distance. To obtain the average
ally will not give accurate calculated SPLs at very
outdoor SPL at any distance, use equation 8-2 and
close distances to large-size sources, such as cool-
obtain the value of the "distance term" from
ing towers. The data of table C-10 may be used
C-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
