DG
Figure 3-7
Lighting Without Glare
c. Veiling Reflections.
C. Acoustic Design.
Lighting shall be designed so as to minimize veiling
reflections; that is, light which is reflected off the task
(1) Terminology.
or nearby surfaces directly into the student's eyes. In
Three terms are common to basic discussion of
general, this involves selecting and placing the light
acoustic design in Service Schools: Decibel (db), Noise
fixture so that the angle of incidence measured from
Reduction Coefficient (NRC) and Sound Transmission
the vertical is greater than 30 degrees, with as much
Class (STC). Decibel is a measure of intensity of
light as possible falling within the 30 to 60 degree
sound related to its subjective loudness. For measuring
core. (Figure 3-6).
ordinary sounds, a decibel level of zero represents the
faintest sound audible to the average person. Normal
voice conversation is approximately 60 db to 80 db.
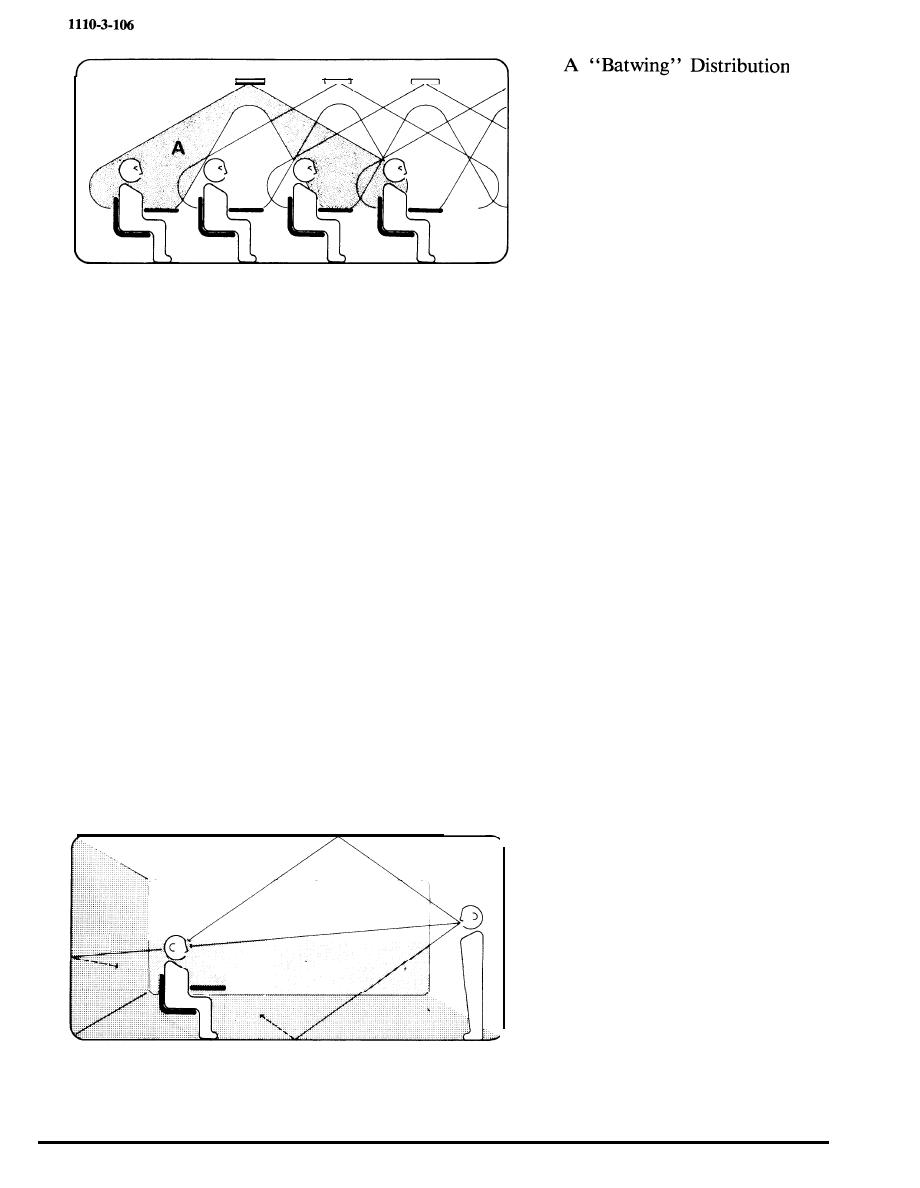
d. Glare.
Noise Reduction Coefficient is a mathematical average
Lighting design shall also minimize glare; that is, light
of sound absorption coefficients recorded at the
which shines directly from the light source into the
frequencies of 250, 500, 1,000 and 2,500 cycles per
student's eyes. This can be accomplished by selecting
second. The use is to quantify sound systems for
and placing light fixtures so as to direct the light
comparison. Sound Transmission Class is a rating
below a 60 degree angle of incidence, with, again, as
based on standardized test performance for evaluating
much light as possible falling in the 30 to 60 degree
the effectiveness of assemblies in isolating airborne
core. Lighting fixtures with low brightness
sound transmission. A frequency range of 113 to 4,450
characteristics that produce a "bat-wing" light
cycles per second is included for the standardized test.
distribution pattern are one means of satisfying this
requirement. (Figure 3-7).
(2) Maximum Sound Level.
Loud and sustained noise can be a hazard to hearing.
e. Audio-Visual Presentation.
The safe limit for an unprotected ear is approximately
Lighting design for A-V presentation is discussed in
3-4.f.
Sound Reflective Surfaces
Indicated in White
Sound Absorptive Surfaces
Indicated in Tone
Figure 3-8
Room Sound Control
3-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
