I
DG 1110-3-106
located near the screen, easy to operate, and allow
(5) Full and Partial Viewing Sectors.
complete control by a single person.
For a given screen size, using the maximum viewing
area permits a greater number of seats than does a
(2) Lighting Levels.
partial viewing sector; however, it results in less
Room ambient light level should be between 10% and
efficient utilization of space, as only 30% of the room
33% of the screen (or tube) brightness. Recommended
can be occupied by seats. By using a more rectangular
ambient light levels for particular media and output
room, seating area is decreased by one-third, but room
sources are:
space is utilized more efficiently: seats may occupy
Media
Source
40% of the room. (Figure 3-19). Furthermore, the
Normal
High-Output
seating eliminated by this arrangement is that portion
15-25 fc
16mm film
5-10 fc
of the seating located along the least desirable viewing
15-25 fc
25-35 fc
35mm slides
angles.
Videotape Projected
Television
35 fc
4-10 fc
F. Lighting Design for A-V Presentation.
G. Ventilation.
(1) Controls.
Criteria and design of mechanical systems for A-V
Room lighting must be controlled for different media
rooms shall be identical to the classrooms served.
and viewer tasks. The controls must be conveniently
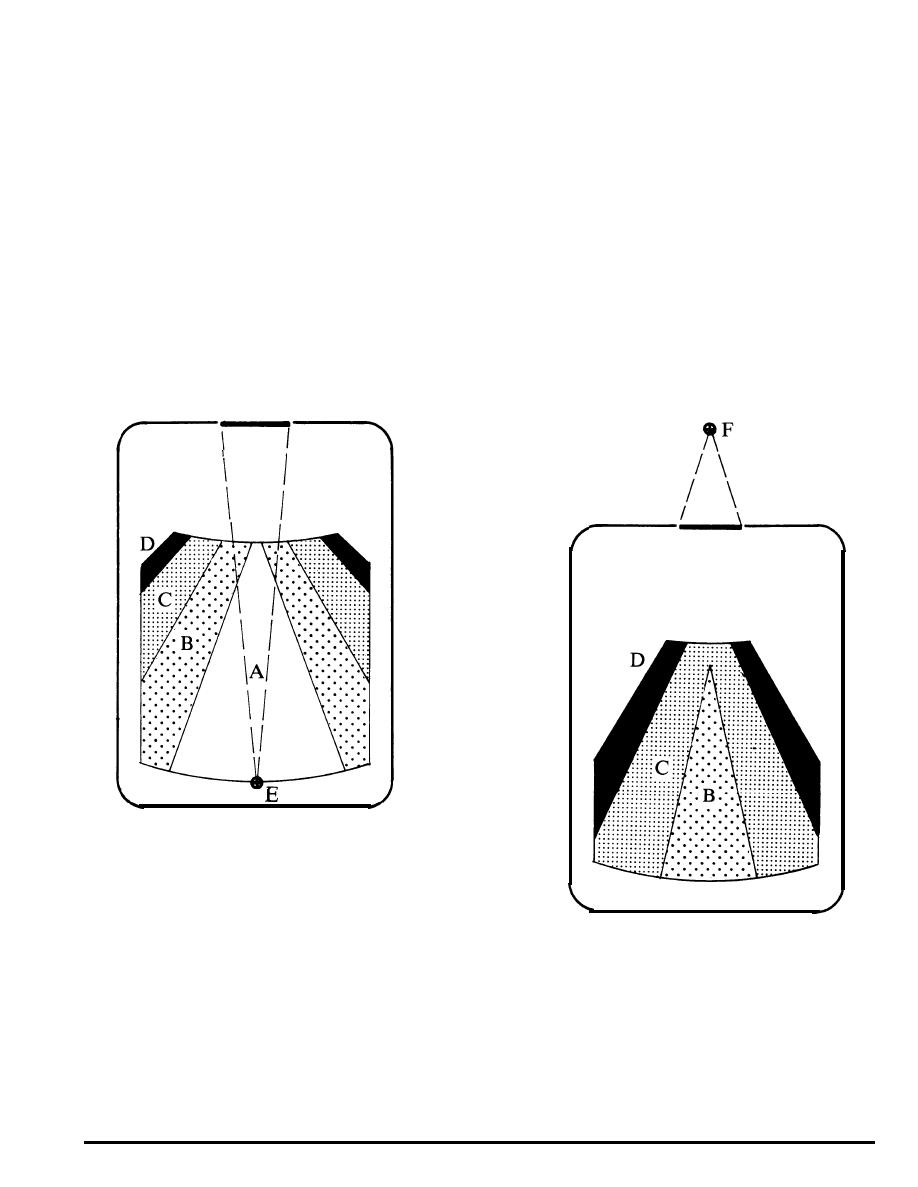
Front Projection
A Excellent
B Very Good
C Good
Rear Projection
D Fair
E Front Projection Source
F Rear Projection Source
Figure 3-17
Comparison of Image Quality,
Front and Rear Screen Systems.
3-15



 Previous Page
Previous Page
