EXAMPLE DESIGNS
DG 1110-3-112 May 1979
6-2 EXAMPLE DESIGN-SCHEME A FOR 6,000 MILITARY STRENGTH (cont'd)
d. DESIGN SOLUTION
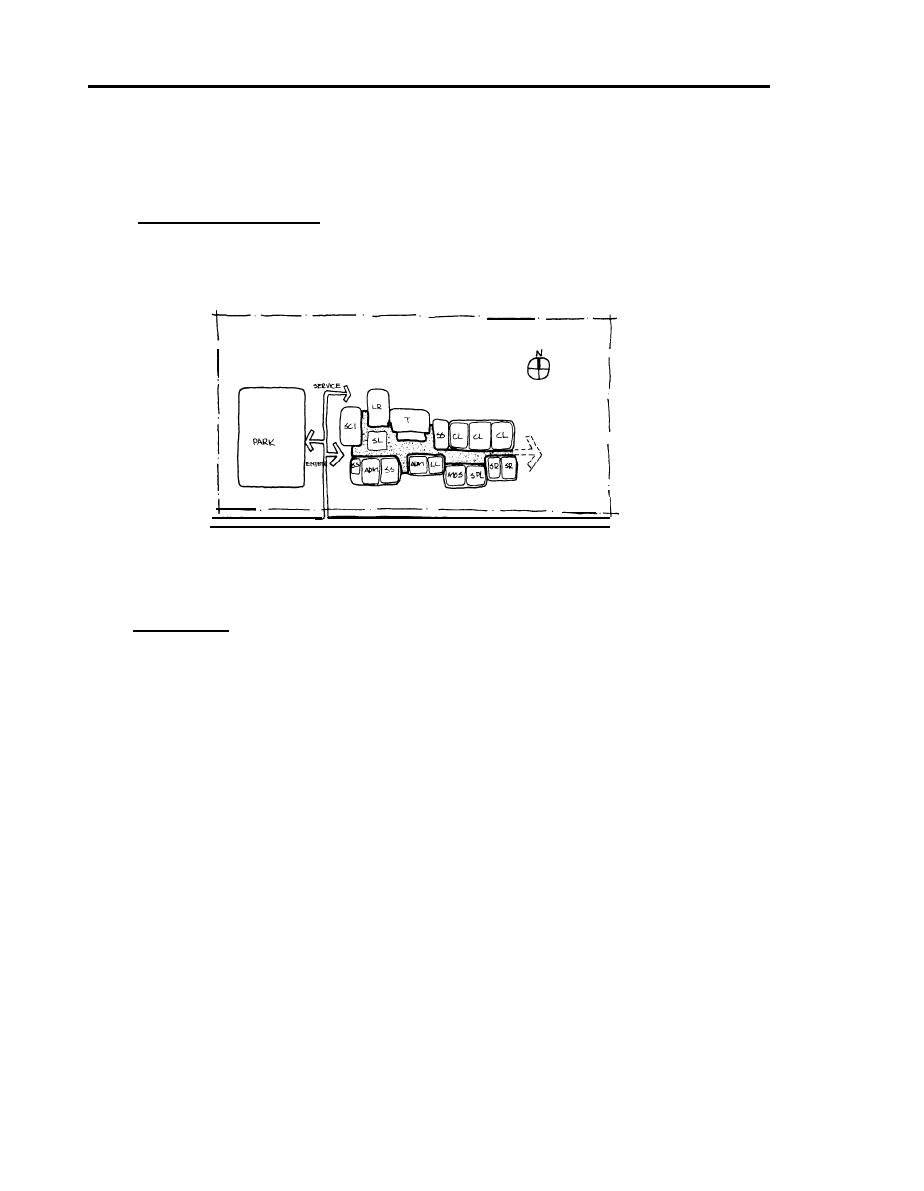
(1) Basic Spatial Organization. Since this example project does not include vocational training
spaces and must be designed to fit on a long, narrow site, a simple linear scheme, modified from the
parallel and axial schemes is used. Primary access is provided at one end which adjoins the parking
area as shown in Figure 6-1.
Figure 6-1 Basic Spatial Organization-Scheme A
(2) Example PIan. This example design is developed around two courtyards along the primary
circulation spine as shown in Figure 6-2. The courtyards are used to create volumetric interest in
conjunction with a set of viewing positions planned along the scheme. They are also used to provide
natural light and greenery to the interior of the building, creating focal points around which various
functional spaces are clustered. The information/registrar area is located adjacent to the main
entrance to serve as a control point for the building. The student lounge is located on the circulation
spine adjacent to the vending area and the lecture room for multi-use purposes. Counselor offices are
centrally located for easy access from the main entrance to serve the needs of both students enrolled
in courses and military personnel who come for counseling only. Toilets are placed at the approximate
center of the circulation spine in order to best serve the entire building. Employing the basic 5-foot
module system discussed in Chapter 3., the 25 ft x 30 ft (750 SF) module is utilized for all academic
and staff spaces. The modules are offset at various points to create the interior courtyard spaces.
6-8



 Previous Page
Previous Page
