Chapter 7
b. Programmed Spaces Module
(1) Meeting Spaces
(a) Description. The meeting spaces will be used pri-
marily for scheduled group activities, clubs and meetings,
classes, dances/music/gymnastics instruction and prac-
tice, and supervised free play for children. The meeting
spaces should also accommodate overflow of activities
such as crafts, team organization meetings,-or watching
special events on television. Also, because these
spaces can be secured, they can be used for dressing
areas for dramatic groups, rehearsal areas for plays and
performances, or places where scenery and equipment
might be assembled and stored for a short time.
(b) Space Allocation. See Table 7 - 102.
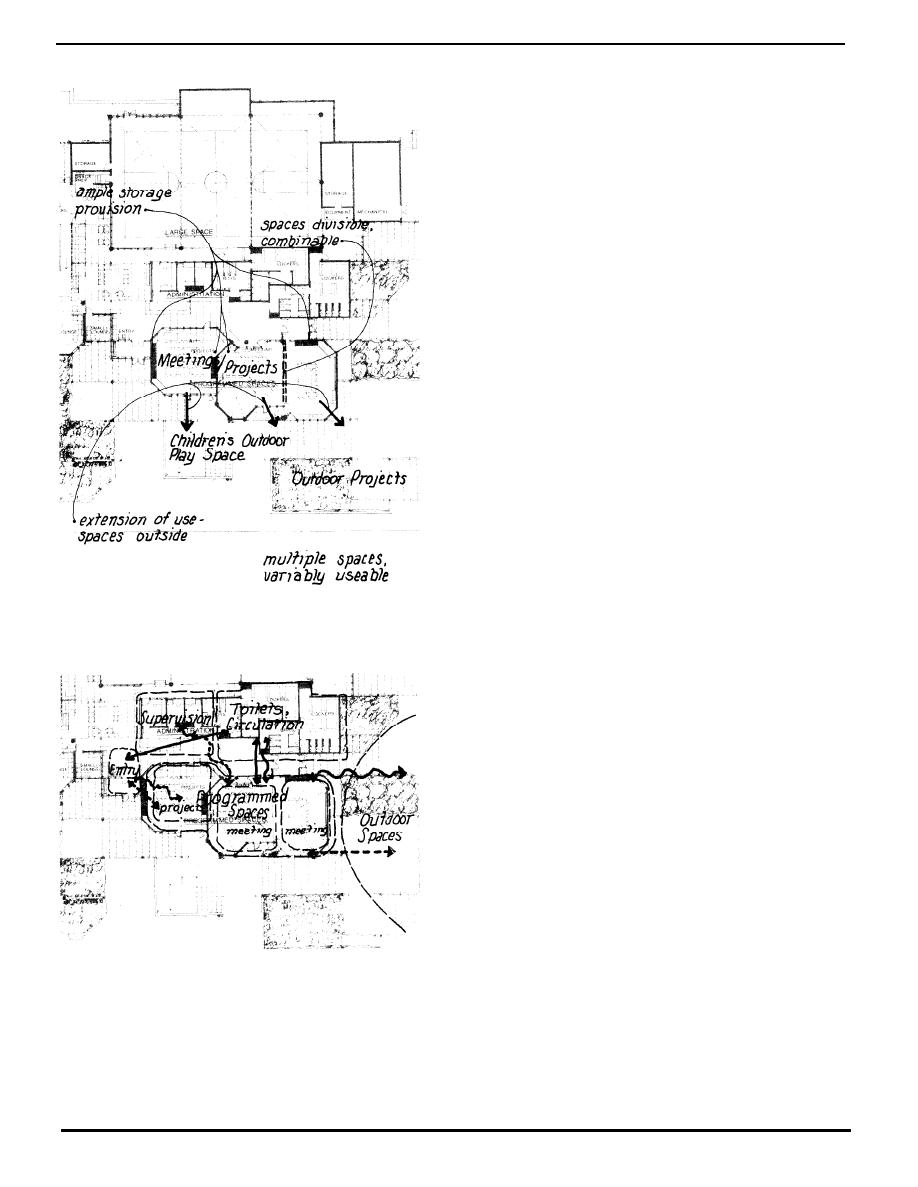
(c) Relationships. The meeting spaces should be
reached indirectly from most other spaces in the center.
However, they must have direct access to the general
storage, toilet areas, locker rooms, entry, and supervision
space. Controlling access to these spaces by direct vis-
ual supervision is important. Where two meeting rooms
are provided, they must be acoustically isolated from the
rest of the center and from each other.
Programmed Spaces Considerations
(2) Projects Space
(a) Description. The projects space has two primary
uses, a place for instruction and a place for individual
projects. The projects room should house only small
projects and be equipped with light tools. For heavier
work, youth activities is expected to utilize other Morale
Support Activities facilities.
(b) Space Allocation. See Table 7 - 101.
(c) Relationships. The projects room must be acousti-
cally separated from the other spaces in the center, and
have access to the general storage and toilet facilities (at
least through a common circulation area). Its products
and activity should be visible to other visitors and users
of the facility, its hours of use could be lengthened if it
were supervised by outside control. It should also have
access to outdoor space for larger projects.
Programmed Spaces Relationships
Page 7-92 DG 1110-3-142



 Previous Page
Previous Page
