TM 5-805-4/AFJMAN 32-1090
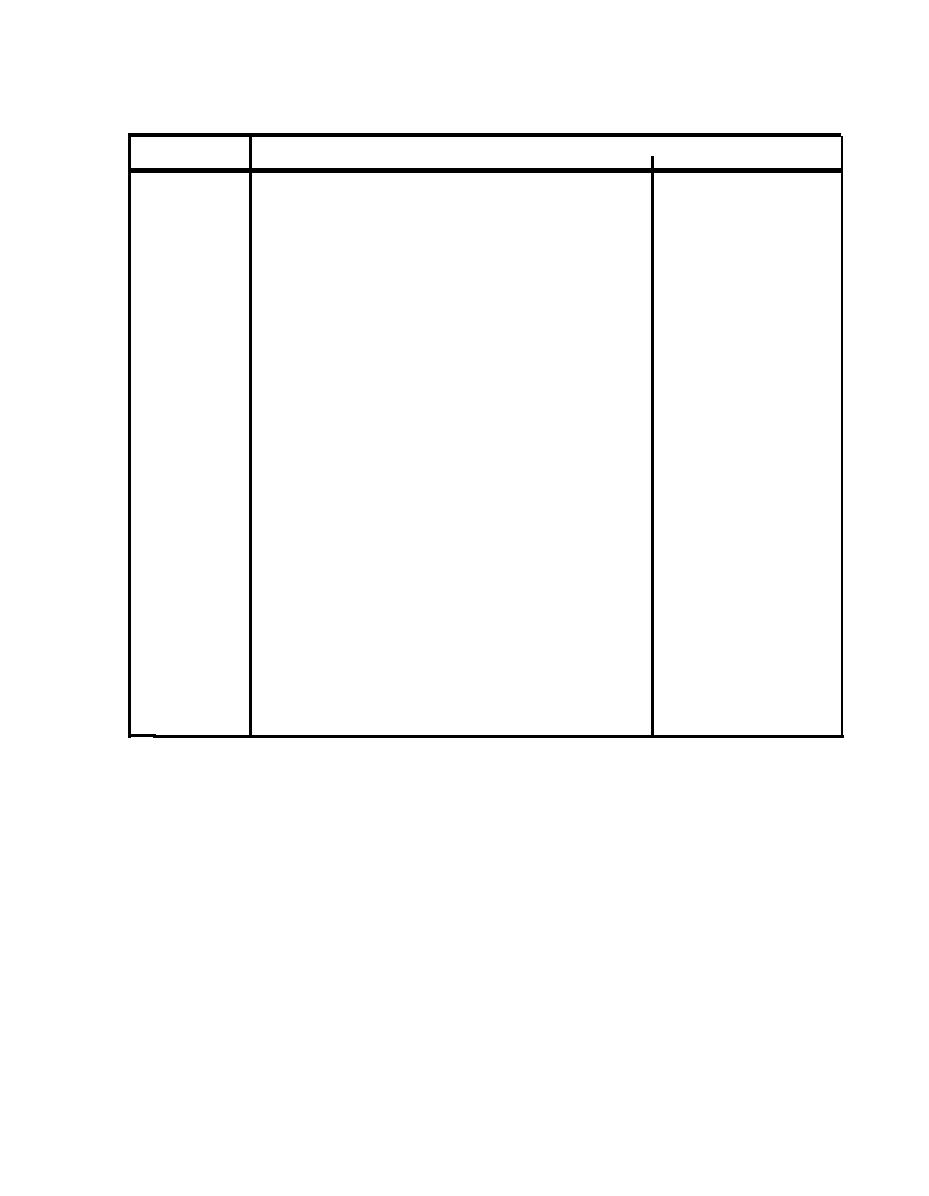
Table 2-1. Category Classification and Suggested Noise Criterion Range for Intruding Steady-State Noise as Heard in Various
Indoor Functional Activity Areas.
a
Noise Criterion
Category
Area (and Acoustic Requirements)
NC-20
1
Bedrooms, sleeping quarters, hospi-
to
tals, residences, apartments,
NC-30
hotels, motels, etc. (for sleeping,
resting, relaxing).
NC-15
2
Auditoriums, theaters, large meeting
to
rooms, large conference rooms, radio
NC-30
studios, churches, chapels, etc.
(for very good listening conditions).
NC-30
Private offices, small conference
3
to
rooms, classrooms, libraries, etc.
NC-35
(for good listening conditions).
NC-35
4
Large offices, reception areas,
to
retail shops and stores, cafeterias,
NC-40
restaurants, etc. (for fair listening
conditions).
NC-40
Lobbies, drafting and engineering
5
to
rooms, laboratory work spaces, main-
NC-50
tenance shops such as for electrical
equipment,etc. (for moderately fair
listening conditions).
NC-45
Kitchens, laundries, shops, garages,
6
to
machinery spaces, power plant control
NC-65
rooms, etc. (for minimum acceptable
speech communication, no risk of
hearing damage).
2-3. Vibration Criteria In Buildings.
the sound level criteria should be even lower than
the criteria normally considered applicable. This
Structural vibration in buildings, which results in
criteria given above is intended to be illustrative;
feelable vibration, produces structural or superfi-
any occupied or habitable area not identified in
cial damage of building components or interferes
the list can be assigned to one of these categories
with equipment operation is unacceptable. In addi-
on the basis of similarity to the types of areas
tion large building components that vibrate can
already listed. Generally, where a range of criteria
produce unacceptable sound levels.
is given, the lower values should be used for the
a. Vibration criteria for occupants. Figure 2-3
more critical spaces in the category and for non-
shows the approximate occupant response to build-
military areas outside the control of the facility;
ing vibration levels. An approximation of the
the higher of the range of criteria may be used for
"threshold of sensitivity" of individuals to feelable
the less critical spaces in the category. Certain
vibration is shown by the shaded area of figure
short-term infrequent sounds (such as the weekly
2-3, labeled "barely perceptible." Other typical
testing of a fire pump or an emergency power
responses of people to vibration are indicated by
generator) may be allowed to exceed normal crite-
the other zones in figure 2-3. These reactions or
ria in relatively noncritical areas as long as the
interpretations may vary over a relatively wide
normal functions of these areas are not seriously
range for different individuals and for different
restricted by the increase in noise.
ways in which a person might be subjected to
2-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
