UFC 4-021-02NF
27 September 2006
change 1, 23 October 2006
2-4
SYSTEM COMPLEXITY
2-4.1
General. ESS can range from simple to complex systems. While there may
be some different views or definitions of what constitutes a simple or a complex system,
this guide will use the criteria described in this section. The definitions used are an
academic basis for presenting different system configurations and integration needs
rather than standardized industry terminology, which does not exist for defining system
complexity.
2-4.2
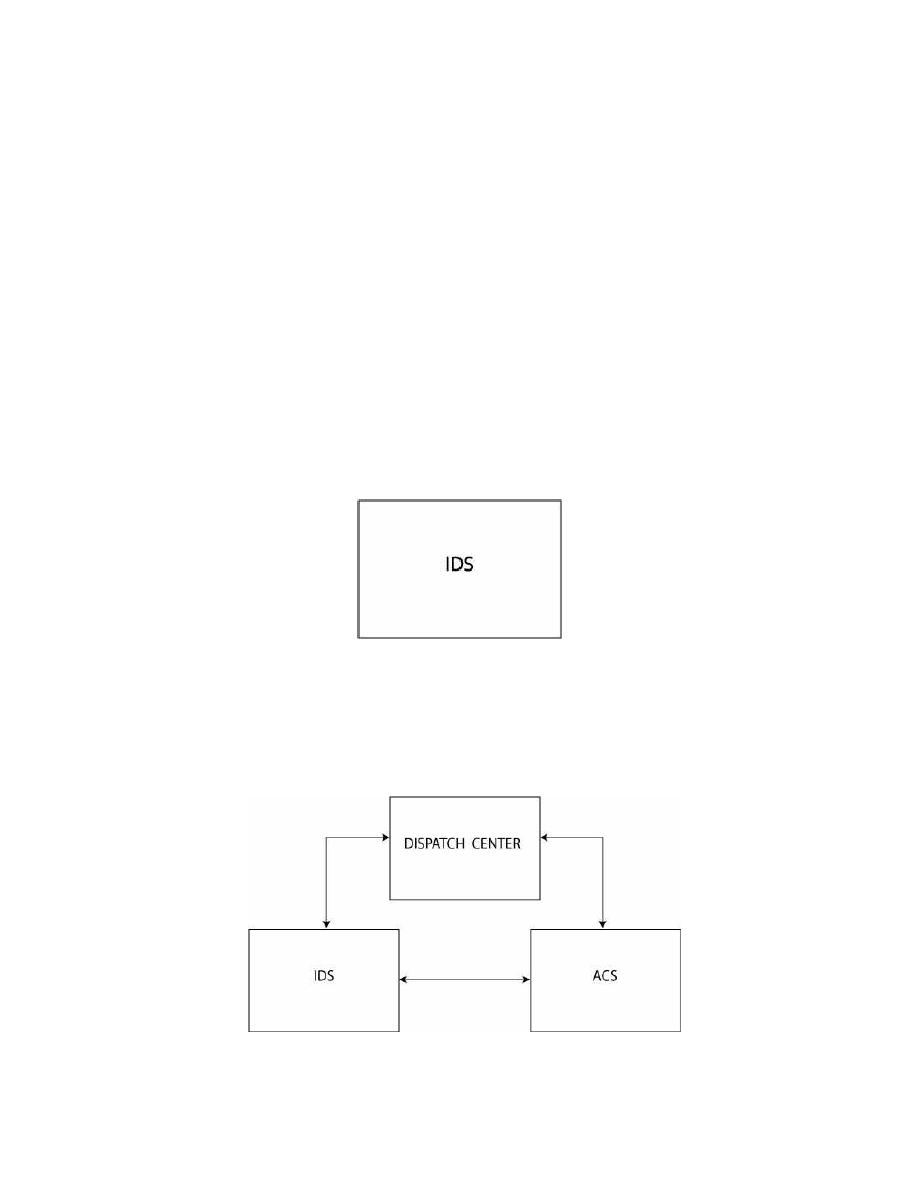
Simple System. The simplest ESS consists of a single ESS subsystem. For
example, a simple IDS at a low value asset is a simple system as shown in Figure 2-5.
Other examples are an IDS with door contact, motion sensors, break-glass sensors and
other digital input type sensors that do not require integration with another ESS
subsystem. Another example of a simple system would be a basic CCTV system of two
cameras going to a Digital Video Recorder (DVR). Figure 2-5 shows a block diagram of
a simple system.
Figure 2-5. A Simple ESS System
2.4.3
Intermediate System. An intermediate system contains elements of at least
two ESS subsystems requiring integration. One example would be an ESS system
requiring both an ACS and an IDS. A basic block diagram for this type of system
reporting to a common Dispatch Center is shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6. Intermediate System with Separate ACS and IDS
18



 Previous Page
Previous Page
