TM 5-815-1/AFR 19-6
particles leave the combustion chamber with the flue
Desulfurization efficiency of a shallow bed is poor,
gases so that solids recirculation is necessary to main-
with only about 60 to 80 percent removal, because SO2
does not have adequate time to react with the limestone
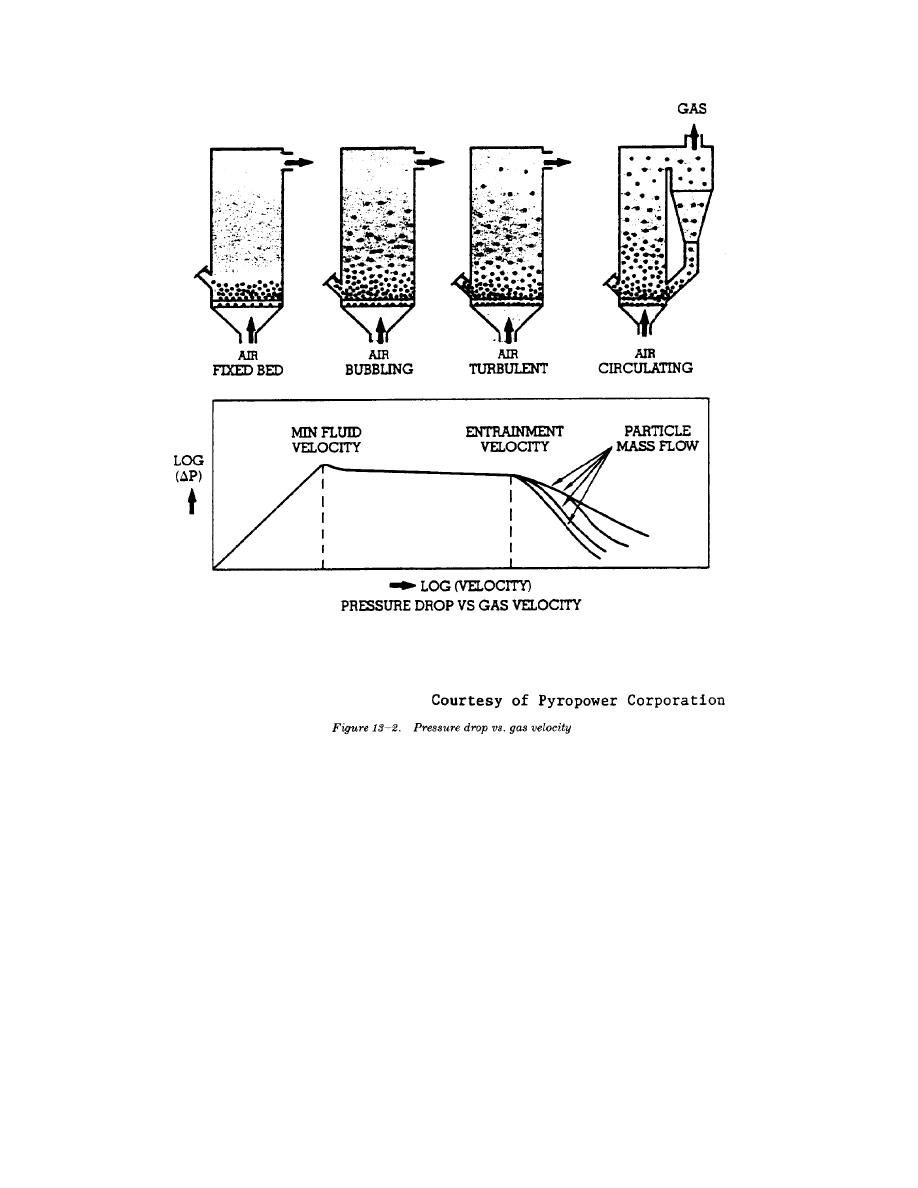
tain the bed solids. This type of fluidization is called
circulating fluidized bed.
before moving out of the shallow bed. The shallow bed
e. The mean solids velocity increases at a slower rate
fluidized boiler is of the bubbling bed design. The shal-
than does the gas velocity, as illustrated in figure 13-3.
low bed will be of very limited use because of its poor
Therefore, a maximum slip velocity between the solids
sulfur dioxide removal.
g. A deep fluidized bed boiler is a bubbling bed
and the gas can be achieved resulting in good heat
transfer and contact time with the limestone, for sulfur
design.
dioxide removal. When gas velocity is further
(1) The bed depth is usually 3 feet to 5 feet deep
increased, the mean slip velocity decreases again.
and the pressure drop averages about one
These are the operating conditions for transport reactor
inch of water per inch of bed depth. The bulk
or pulverized coal boiler. The design of the fluidized
of the bed consists of limestone, sand, ash, or
bed falls between the stoker fired boiler and the pul-
other material and a small amount of fuel.
verized coal boiler using the bed expansion.
The rate at which air is blown through the bed
f. The shallow fluidized bed boiler operates with a
determines the amount of fuel that can be
single bed at a low gas velocity. A shallow bed mini-
reacted. There are limits to the amount of air
mizes fan horsepower and limits the free-board space.
that can be blown through before the bed
The bed depth is usually about 6 inches to 9 inches and
material and fuel are entrained and blown out
the free-board heights are only four to five feet.
13-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
