DG 1110-3-106
available from the most recent Manpower Survey
continuing requirement for large amounts of dedicated
Report, and Training Base Review (TBR) statistics.
special purpose classroom space; however, the necessity
for dedicated classrooms can be minimized by
providing as high a degree of flexibility in general
F. Instructional Support.
While the common teaching method of lecture and
classroom design and equipment as possible.
testing is applied widely in many courses, the use of
visible, audible, and manipulative ("hands-on")
G. Unique Characteristics.
training aids has been a tradition in Army training.
Consequently, use of training devices in Army schools
(1) Frequent Changes in Instructional Program and
has reached a high level in scope and sophistication.
Student Load.
Training devices include actual army equipment, full
Since much service school instruction involves training
scale mock-ups, simulation models, programed display
in the use and maintenance of Army equipment,
panels, motion pictures, cable and cassette TV systems,
changes in this equipment or in the procedures
recordings, programed self-instruction casette and
governing its use require corresponding changes in
computer terminals, graphics, felt boards, multi-
instructional programs. Changes in student load due to
frequency lighting, etc. Depending on the size, nature,
changing Army manpower requirements are also
and complexity of these devices, classrooms might
common. The number of students in training may
become more or less "dedicated" in order to
vary widely between successive classes, and this
accommodate their usage. It is expected that the trend
situation often occurs with little advance notice.
toward sophisticated training devices will result in a
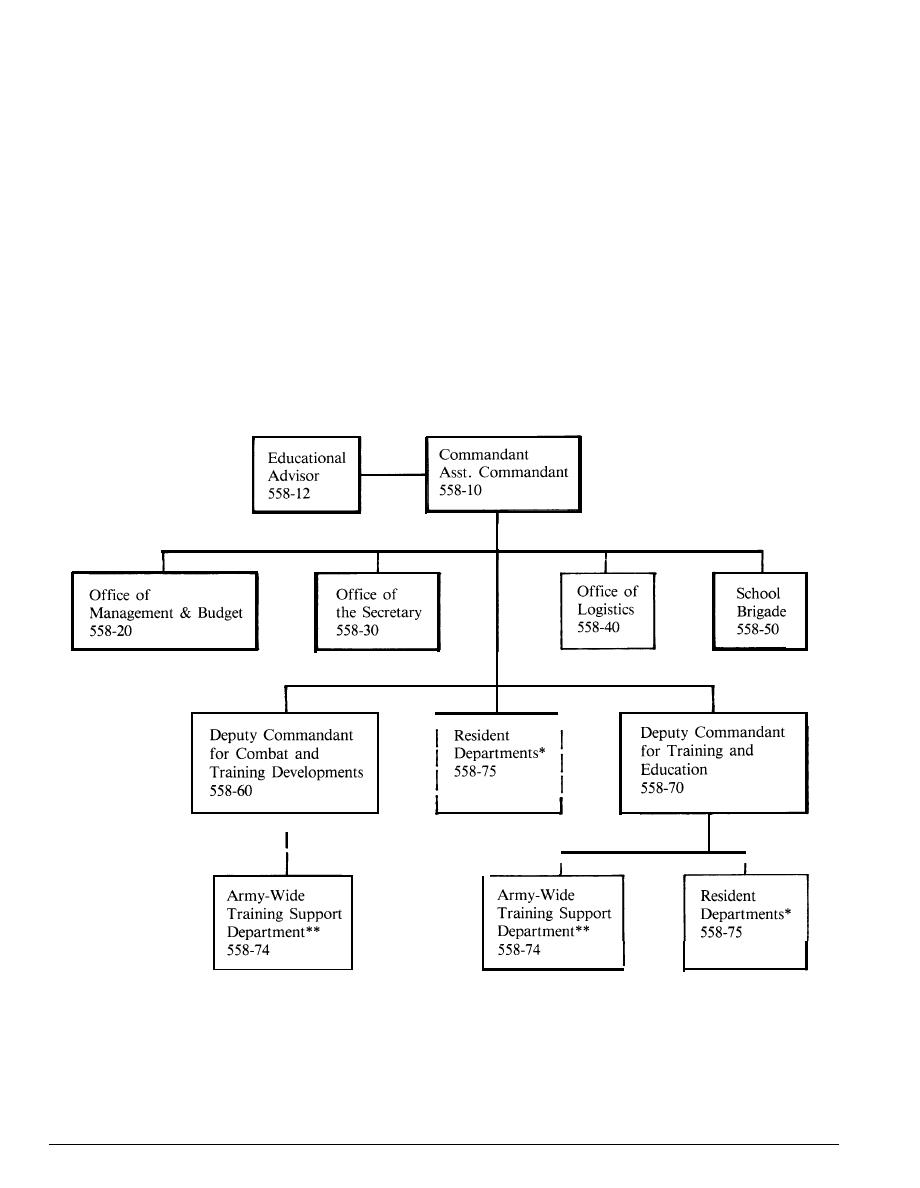
*Resident Departments may optionally be organized under the Office of the Commandant
**Army-Wide Training Support Department may optionally be placed under the Deputy Commandant for
Combat and Training Developments
Figure 2-1
U.S. Army Service School Organization Chart
2-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
